Venture debt and equity are two financing options that are commonly used by startups to raise capital. While equity involves giving up ownership stakes in the company, venture debt allows startups to borrow money with interest rates and repayment terms. But many people wonder, “Wouldn’t venture debt be more expensive than equity?”
The truth is, both financing options have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the cost of each depends on various factors. In this article, we will explore the differences between venture debt and equity and examine whether venture debt is truly more expensive than equity. So, let’s dive in!
Understanding the Cost of Venture Debt vs. Equity
What is Venture Debt?
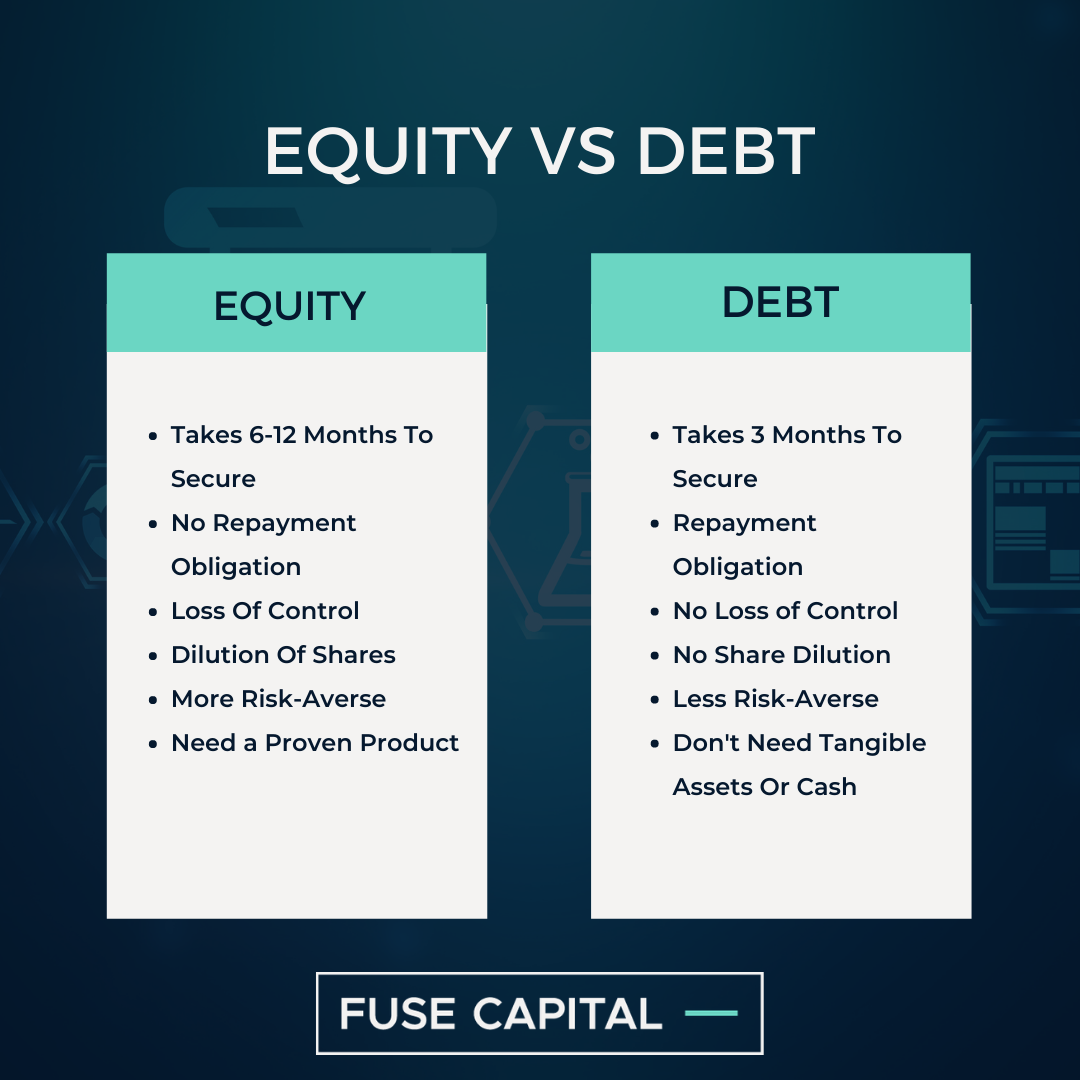
Venture debt is a type of financing that provides companies with additional funding without diluting ownership. It is typically provided by specialty lenders and can be a good alternative to equity financing, especially for companies that are not yet profitable. The cost of venture debt is generally higher than traditional bank loans, but lower than equity financing.
Venture debt typically comes with a fixed interest rate, and the lender may also receive warrants, which give them the option to purchase shares of the company at a discounted price. This can be a good way for lenders to participate in a company’s growth potential, while also providing the company with much-needed funding.
Benefits of Venture Debt
– No dilution of ownership: Venture debt allows companies to raise additional funds without giving up ownership or control.
– Flexible terms: Venture debt can be structured in a variety of ways to meet the needs of the company.
– Faster access to funds: Venture debt can be obtained more quickly and with less paperwork than equity financing.
Disadvantages of Venture Debt
– Higher interest rates: The cost of venture debt is generally higher than traditional bank loans.
– Collateral requirements: Venture debt lenders may require collateral, such as intellectual property or accounts receivable.
– Limited funding: Venture debt is typically only available to companies that have a solid revenue stream and a clear path to profitability.
What is Equity Financing?
Equity financing is when a company raises money by selling ownership shares to investors. This can be done through private placements, initial public offerings (IPOs), or other types of offerings. The cost of equity financing is typically lower than venture debt, but it comes with the trade-off of giving up ownership and control.
Equity financing typically comes with a variable cost, as the value of the shares can fluctuate over time. Investors may also require a seat on the company’s board of directors, which can impact decision-making.
Benefits of Equity Financing
– Lower cost: The cost of equity financing is typically lower than venture debt.
– No collateral requirements: Equity financing does not require collateral, which can be a benefit to companies with limited assets.
– Access to expertise: Equity investors may bring valuable expertise and connections to the company.
Disadvantages of Equity Financing
– Dilution of ownership: Equity financing requires companies to give up ownership and control.
– Variable cost: The value of equity shares can fluctuate over time, which can impact the company’s financial stability.
– Greater reporting requirements: Publicly traded companies have greater reporting requirements than private companies.
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
Both venture debt and equity financing have their pros and cons, and companies should carefully consider their options before deciding which route to take. In general, venture debt may be a better option for companies that are not yet profitable, while equity financing may be a better option for companies that are further along in their growth trajectory.
Cost Comparison
The cost of venture debt is generally higher than traditional bank loans, but lower than equity financing. According to a study by the National Venture Capital Association, the average interest rate on venture debt is around 12%, while the average cost of equity financing is around 25%.
Ownership Comparison
Venture debt allows companies to raise additional funds without giving up ownership or control, while equity financing requires companies to give up ownership and control in exchange for funding.
Risk Comparison
Venture debt lenders are typically more risk-averse than equity investors, which means they may require collateral and have stricter lending requirements. Equity investors are more willing to take on risk in exchange for higher potential returns.
Conclusion
Both venture debt and equity financing can be viable options for companies looking to raise additional funds. Companies should carefully consider the pros and cons of each option, as well as their specific needs and growth trajectory, before making a decision. In general, venture debt may be a better option for companies that are not yet profitable and want to avoid dilution of ownership, while equity financing may be a better option for companies that are further along in their growth trajectory and are willing to give up ownership and control in exchange for funding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is specifically designed for startups and early-stage companies. It is typically offered by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of these types of businesses. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is often structured as a flexible line of credit that can be drawn down as needed, providing startups with the cash flow they need to grow and scale their business.
How does venture debt differ from equity?
While venture debt and equity are both ways to raise capital for a startup, they are very different in terms of structure and cost. Equity financing involves selling a portion of the company to investors in exchange for cash, while venture debt is a loan that must be repaid with interest. Equity investors are typically looking for a high return on their investment, which can put pressure on the company’s management team to deliver results quickly. Venture debt, on the other hand, is less dilutive and can be a more cost-effective way to raise capital.
What are the advantages of venture debt?
Venture debt can offer a number of advantages for startups and early-stage companies. For one, it can provide a flexible source of capital that can be used to fund growth initiatives without diluting the ownership of the company. Additionally, venture debt lenders are often more willing to take on risk than traditional banks, which can make it easier for startups to obtain the financing they need. Finally, venture debt can be a more cost-effective way to raise capital than equity financing, since interest rates are typically lower than the cost of selling equity.
What are the disadvantages of venture debt?
While venture debt can be a useful tool for startups, it does have its drawbacks. One of the biggest disadvantages of venture debt is that it must be repaid with interest, which can put a strain on the startup’s cash flow. Additionally, venture debt lenders may require personal guarantees from the company’s founders or other assets as collateral, which can be risky for the management team. Finally, venture debt lenders may also impose restrictive covenants on the company, which can limit its ability to operate and grow.
When is venture debt a good option?
Venture debt can be a good option for startups and early-stage companies that need capital to fund growth initiatives but don’t want to dilute the ownership of the company. It can also be a good option for companies that have a clear path to profitability and can comfortably service the debt. Finally, venture debt can be a good option for companies that are looking to bridge a short-term cash flow gap, since it can be structured as a flexible line of credit that can be drawn down as needed.
The Value of Venture Debt Explained – Trinity Capital Inc.
In conclusion, it is important to understand that venture debt and equity are two different forms of financing and cannot be directly compared in terms of cost. While equity is more expensive in the long run due to the dilution of ownership, venture debt may have higher upfront costs and interest rates. However, venture debt can also provide companies with the flexibility to grow without giving up equity or control.
It is also important to note that the cost of venture debt varies depending on the risk profile of the company, as well as the terms of the loan. Companies with strong fundamentals and a clear growth plan may be able to negotiate better terms and lower interest rates, making venture debt a more cost-effective option.
Ultimately, the decision between venture debt and equity financing should be based on the specific needs and goals of the company. While venture debt may be more expensive in certain cases, it can also provide valuable benefits that make it a worthwhile investment for many growing companies.
