Venture debt is a type of financing that has been gaining popularity among startups in recent years. Unlike traditional equity financing, venture debt involves borrowing money from a lender, typically a bank or a specialized venture debt firm, and paying it back over a set period of time with interest. But what is the average amount of venture debt in a deal, and how does it compare to other types of financing?
The answer is not straightforward, as the amount of venture debt in a deal can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the stage of the startup, its revenue and growth potential, and the lender’s appetite for risk. However, by understanding the basics of venture debt and the factors that affect its terms, startups can make informed decisions about their financing options and optimize their capital structure for growth.
What is the Average Amount of Venture Debt in a Deal?
Venture debt is a type of financing that is often used by startups and early-stage companies to supplement equity financing. It is a loan that is secured by the assets of the company, and it is designed to provide additional capital without diluting the ownership of the company. The amount of venture debt that a company can raise depends on several factors, such as the company’s stage of development, its revenue, and its growth prospects.
Understanding Venture Debt
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is provided to startups and early-stage companies. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of startups and are willing to take on more risk. Venture debt is often used to supplement equity financing, which is the primary source of funding for startups.
Venture debt is typically structured as a term loan with a fixed interest rate and a set repayment schedule. It is secured by the assets of the company, such as its intellectual property, equipment, or accounts receivable. Venture debt lenders also often require warrants, which are rights to purchase equity in the company at a future date.
The Average Amount of Venture Debt
The amount of venture debt that a company can raise depends on several factors. One of the most important factors is the stage of development of the company. Early-stage companies may be able to raise venture debt of up to $5 million, while more mature companies may be able to raise much larger amounts, up to $100 million or more.
Another important factor is the revenue of the company. Lenders typically require that a company have some level of revenue before they will provide venture debt. The amount of revenue required varies depending on the lender, but it is typically in the range of $5 million to $10 million per year.
Growth prospects are also an important factor in determining the amount of venture debt that a company can raise. Companies that have strong growth prospects and a clear path to profitability may be able to raise larger amounts of venture debt.
Benefits of Venture Debt
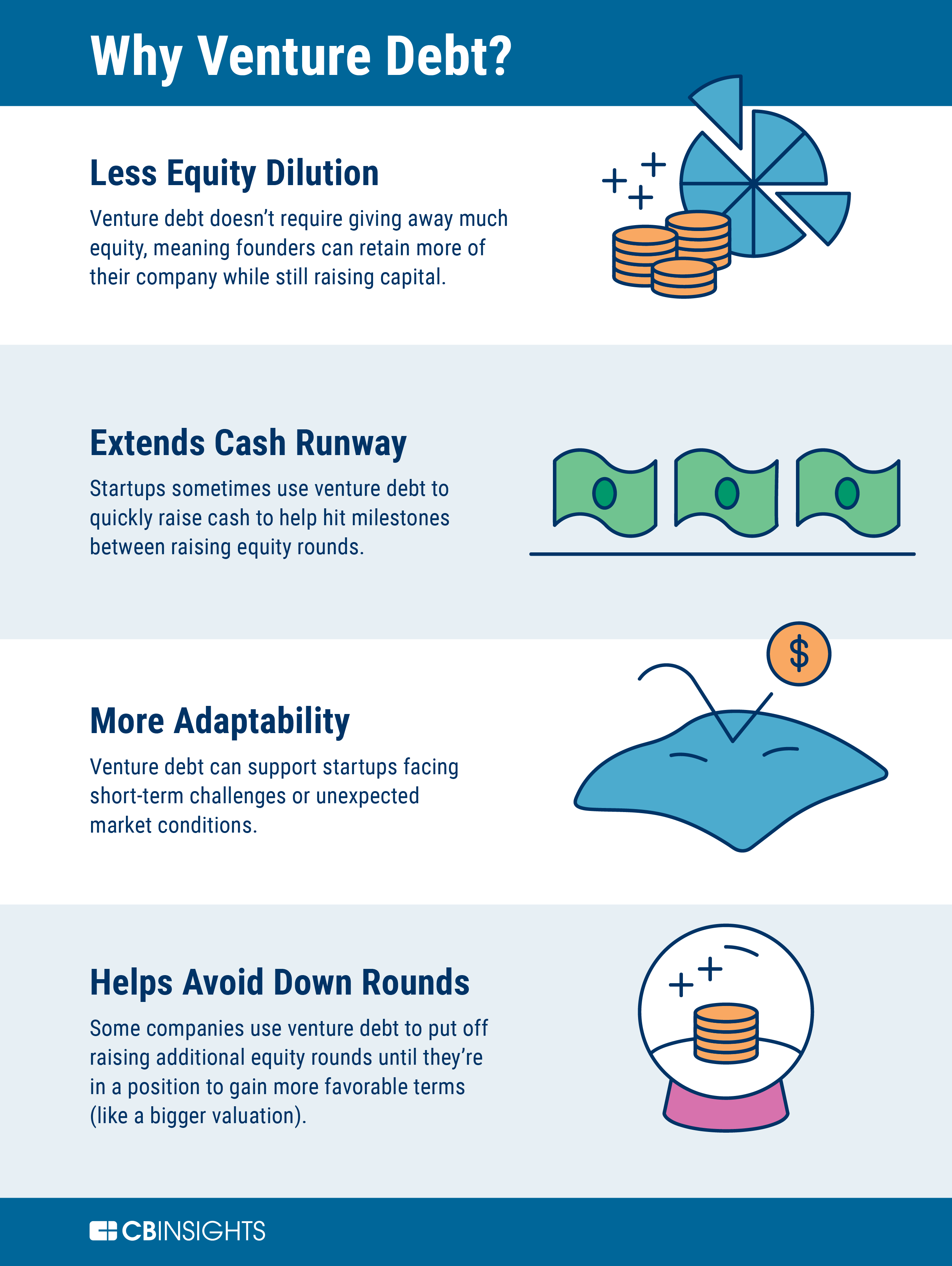
Venture debt can provide several benefits to startups and early-stage companies. One of the most important benefits is that it allows companies to raise additional capital without diluting the ownership of the company. This is particularly important for founders and early investors who want to maintain control of the company.
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can be less expensive than equity financing. Equity financing often requires that a company give up a significant portion of its ownership in exchange for capital. Venture debt, on the other hand, is a loan that is repaid with interest.
Venture debt can also provide companies with more flexibility than equity financing. Equity financing often comes with restrictions on how the capital can be used and when it must be repaid. Venture debt, on the other hand, is typically more flexible and can be used for a variety of purposes, such as funding growth initiatives or acquiring new customers.
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
Venture debt and equity financing are two different types of financing that can be used by startups and early-stage companies. While both types of financing can provide capital to a company, there are some important differences between them.
Equity financing involves selling ownership in the company in exchange for capital. This means that the investors become shareholders in the company and are entitled to a portion of the profits. Equity financing can be more expensive than venture debt because it involves giving up ownership in the company.
Venture debt, on the other hand, is a loan that is secured by the assets of the company. This means that the lender does not own a stake in the company and is not entitled to a portion of the profits. Venture debt can be less expensive than equity financing because it does not involve giving up ownership in the company.
In summary, venture debt is a type of financing that can provide additional capital to startups and early-stage companies without diluting the ownership of the company. The amount of venture debt that a company can raise depends on several factors, such as the stage of development, revenue, and growth prospects. Venture debt can provide several benefits, such as flexibility, lower cost, and less dilution of ownership, and can be a good alternative to equity financing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors determine the amount of venture debt in a deal?
The amount of venture debt in a deal depends on various factors. One of the most important factors is the stage of the company. Early-stage companies may receive smaller amounts of venture debt as they have less revenue and are more risky. Other factors include the amount of equity raised, the company’s growth potential, and the overall market conditions.
Another factor that can affect the amount of venture debt is the lender’s risk appetite. Lenders that are more conservative may offer smaller amounts of debt, while lenders that are more aggressive may offer larger amounts.
How does venture debt differ from traditional bank loans?
Venture debt is typically used by startups and high-growth companies that have raised equity financing. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is often unsecured and has higher interest rates. In exchange for the higher risk, venture debt lenders may also receive warrants or equity in the company.
Venture debt can also provide companies with more flexibility than traditional bank loans. It can be used to fund working capital, capital expenditures, and other growth initiatives. Additionally, venture debt lenders may be more willing to work with companies that have not yet achieved profitability.
What are the typical interest rates for venture debt?
The interest rates for venture debt can vary depending on the lender, the stage of the company, and the overall market conditions. Generally, interest rates for venture debt are higher than traditional bank loans and can range from 8% to 20%.
In addition to interest rates, venture debt lenders may also charge fees such as origination fees, prepayment fees, and closing costs. It’s important for companies to carefully review the terms and fees associated with a venture debt deal before accepting it.
What are the advantages of using venture debt?
One of the main advantages of using venture debt is that it can provide additional funding without diluting the company’s equity. This can be especially beneficial for companies that are close to profitability or have limited options for raising capital.
Venture debt can also provide companies with more flexibility than other types of financing. It can be used to fund working capital, capital expenditures, and other growth initiatives. Additionally, venture debt lenders may be more willing to work with companies that have not yet achieved profitability.
What are the risks of using venture debt?
While venture debt can provide additional funding and flexibility, it also comes with risks. One of the main risks is that it can be more expensive than other types of financing. Interest rates and fees can be higher, which can increase the cost of capital for the company.
Additionally, venture debt is often unsecured, which means that the lender does not have a claim on specific assets if the company defaults. This can make it more difficult for the lender to recover their investment in the event of a bankruptcy or other default. Companies should carefully consider the risks and benefits of venture debt before pursuing it as a financing option.
The Value of Venture Debt Explained – Trinity Capital Inc.
In conclusion, venture debt has become an increasingly popular financing option for startups looking to raise capital without diluting their equity. While the amount of venture debt in a deal can vary depending on a number of factors, the industry average is typically around 20-30% of the total funding raised.
However, it’s important to note that venture debt is not a one-size-fits-all solution and should be carefully considered alongside other financing options. Startups should assess their specific needs and goals before deciding on the amount of venture debt to take on.
Ultimately, venture debt can be a valuable tool for startups looking to accelerate their growth and reach their milestones. By leveraging this financing option alongside equity funding and other sources of capital, startups can position themselves for long-term success in today’s competitive market.
