Venture debt has become an increasingly popular way for startups to raise capital without diluting their equity. This type of financing can provide a significant boost to a company’s growth, but it also comes with risks. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at some of the biggest venture debt failures in recent history and explore what we can learn from them.
From high-profile bankruptcies to lesser-known failures, there have been plenty of cautionary tales when it comes to venture debt. Whether it was due to poor management, unexpected market shifts, or simply bad luck, these cases serve as a reminder of the importance of careful planning and risk management in any business venture. Join us as we delve into the stories behind some of the biggest venture debt failures of all time.
What are the Biggest Venture Debt Failures?
Venture debt is a form of financing that provides companies with the necessary funds to grow their business. While it can be a useful tool for many startups, there are also many examples of venture debt failures. These failures can be caused by a variety of factors, including mismanagement, market conditions, and unexpected events. In this article, we will take a look at some of the biggest venture debt failures and what we can learn from them.
1. Jawbone
Jawbone was a consumer electronics company that specialized in wearable fitness trackers and wireless speakers. The company raised over $900 million in venture funding, including $165 million in venture debt. However, despite its success in the early days, Jawbone struggled to keep up with the competition and was eventually forced to shut down in 2017. The company’s failure was due to a combination of mismanagement, market saturation, and increased competition from companies like Fitbit and Apple.
Benefits of Venture Debt
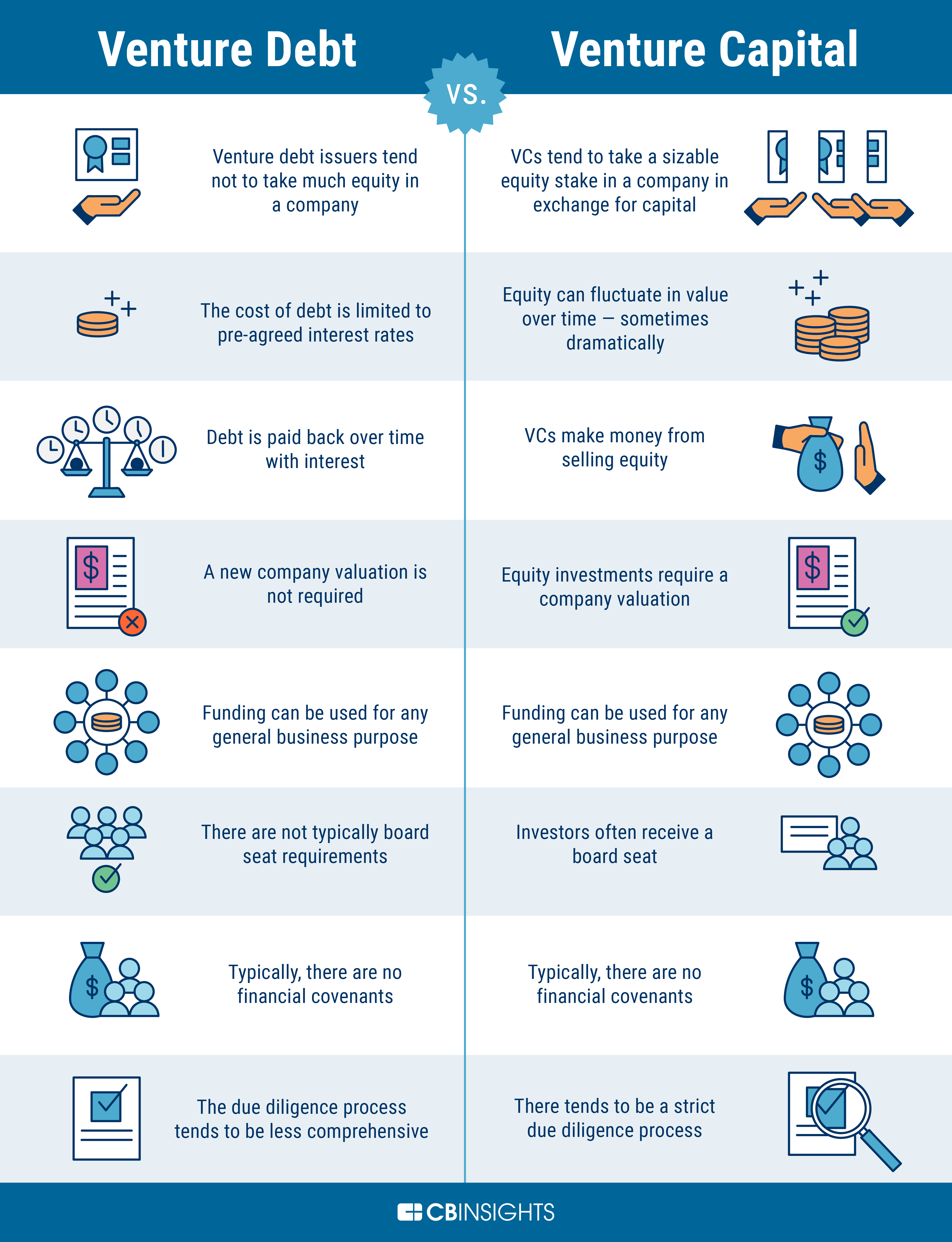
While Jawbone’s failure is a cautionary tale for startups, it’s important to note that venture debt can still be a valuable tool for many companies. One of the biggest benefits of venture debt is that it allows companies to raise capital without giving up equity. This can be especially beneficial for startups that are still in the early stages of growth and want to retain as much ownership as possible.
Vs Equity Financing
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can be less dilutive than equity financing. When a company raises equity financing, it typically has to give up a percentage of ownership in exchange for the capital. With venture debt, however, the company is only required to pay interest on the loan and can retain full ownership of the business.
2. Renovate America
Renovate America was a provider of home improvement financing that raised over $1.5 billion in venture funding, including $300 million in venture debt. The company’s business model was based on providing loans to homeowners for energy-efficient home improvements, which they could pay back over time through their property tax bills. However, the company struggled to keep up with the demand for its services and was eventually forced to lay off a significant portion of its workforce.
Unexpected Events
Renovate America’s failure was due in part to unexpected events, such as changes in the regulatory environment and a decline in the housing market. These factors made it difficult for the company to continue operating and led to its eventual downfall.
Lessons Learned
One of the key lessons learned from Renovate America’s failure is the importance of diversification. By relying too heavily on a single business model, the company was unable to adapt to changing market conditions and was ultimately unable to survive.
3. MoviePass
MoviePass was a subscription-based service that allowed users to see unlimited movies for a monthly fee. The company raised over $68 million in venture funding, including $6.2 million in venture debt. However, the company was unable to sustain its business model and was forced to shut down in 2019.
Market Conditions
One of the main reasons for MoviePass’s failure was the unsustainable nature of its business model. The company was essentially subsidizing the cost of movie tickets for its users, which meant it was losing money on every ticket sold. While this business model may have been viable in the short term, it was not sustainable over the long term.
Competitive Landscape
Another factor that contributed to MoviePass’s failure was the competitive landscape. The company faced competition from other movie subscription services, as well as traditional movie theaters that were beginning to offer their own subscription plans.
4. Blue Apron
Blue Apron was a meal kit delivery service that raised over $200 million in venture funding, including $135 million in venture debt. The company’s business model was based on delivering pre-portioned ingredients and recipes to customers’ homes, allowing them to cook meals without having to go to the grocery store. However, the company struggled to retain customers and was eventually forced to lay off a significant portion of its workforce.
Market Saturation
One of the main reasons for Blue Apron’s failure was market saturation. The company faced competition from other meal kit delivery services, as well as traditional grocery stores that were beginning to offer their own meal kits. This made it difficult for Blue Apron to stand out in a crowded market.
High Customer Acquisition Costs
Another factor that contributed to Blue Apron’s failure was the high cost of acquiring customers. The company spent a significant amount of money on marketing and advertising, which made it difficult to achieve profitability.
5. Quirky
Quirky was a company that allowed inventors to submit their ideas for new products and then helped them bring those products to market. The company raised over $185 million in venture funding, including $30 million in venture debt. However, the company was unable to sustain its business model and filed for bankruptcy in 2015.
Complex Business Model
One of the main reasons for Quirky’s failure was the complexity of its business model. The company had to manage a large number of inventors and products, which made it difficult to scale the business and achieve profitability.
Mismanagement
Another factor that contributed to Quirky’s failure was mismanagement. The company had a highly centralized decision-making process, which made it difficult for employees to make decisions and take action on their own. This slowed down the company’s ability to innovate and respond to changing market conditions.
6. Skully
Skully was a startup that developed a high-tech motorcycle helmet with a built-in heads-up display. The company raised over $15 million in venture funding, including $11 million in venture debt. However, the company was unable to bring its product to market and eventually filed for bankruptcy in 2016.
Production Delays
One of the main reasons for Skully’s failure was production delays. The company struggled to manufacture its product at scale, which delayed its launch and made it difficult to generate revenue.
Funding Issues
Another factor that contributed to Skully’s failure was funding issues. The company had raised a significant amount of money, but it was not enough to sustain the business over the long term. As a result, the company was forced to shut down when it ran out of funding.
7. Fuhu
Fuhu was a company that developed tablets and other electronic devices for children. The company raised over $200 million in venture funding, including $30 million in venture debt. However, the company was unable to compete with larger players in the market and filed for bankruptcy in 2016.
Market Saturation
One of the main reasons for Fuhu’s failure was market saturation. The company faced competition from larger players like Amazon and Apple, which made it difficult to stand out in a crowded market.
High Burn Rate
Another factor that contributed to Fuhu’s failure was its high burn rate. The company spent a significant amount of money on marketing and advertising, which made it difficult to achieve profitability.
8. Rdio
Rdio was a music streaming service that raised over $125 million in venture funding, including $50 million in venture debt. The company was unable to compete with larger players like Spotify and Apple Music and filed for bankruptcy in 2015.
Competition
One of the main reasons for Rdio’s failure was competition. The company faced stiff competition from larger players in the market, which made it difficult to gain market share.
Licensing Costs
Another factor that contributed to Rdio’s failure was licensing costs. The company had to pay significant fees to record labels for the right to stream their music, which made it difficult to achieve profitability.
9. Homejoy
Homejoy was a company that provided on-demand home cleaning services. The company raised over $40 million in venture funding, including $10 million in venture debt. However, the company was unable to achieve profitability and was eventually forced to shut down in 2015.
High Customer Acquisition Costs
One of the main reasons for Homejoy’s failure was the high cost of acquiring customers. The company spent a significant amount of money on marketing and advertising, which made it difficult to achieve profitability.
Regulatory Issues
Another factor that contributed to Homejoy’s failure was regulatory issues. The company faced legal challenges in several states over its classification of workers as independent contractors, which added additional costs and complexity to the business.
10. Grooveshark
Grooveshark was a music streaming service that allowed users to upload and share music with others. The company raised over $6 million in venture funding, including $2 million in venture debt. However, the company faced legal challenges over copyright infringement and was eventually forced to shut down in 2015.
Legal Issues
One of the main reasons for Grooveshark’s failure was legal issues. The company faced several lawsuits over copyright infringement, which made it difficult to continue operating.
Lessons Learned
One of the key lessons learned from Grooveshark’s failure is the importance of respecting intellectual property rights. By allowing users to upload copyrighted material without permission, the company put itself at risk of legal action and ultimately contributed to its downfall.
In conclusion, these examples of venture debt failures highlight the importance of proper management, diversification, and adaptation to changing market conditions. While venture debt can be a useful tool for many startups, it’s important to understand the risks and limitations involved and to approach it with caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about venture debt failures:
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing provided to startups and other high-growth companies that don’t have a long track record of profitability or significant assets to use as collateral. Venture debt typically comes from specialized lenders who are willing to take on more risk in exchange for potentially higher returns.
Venture debt is often used to supplement equity financing and can be used to fund a variety of activities, including product development, expansion into new markets, and working capital needs.
What are some common reasons for venture debt failures?
There are many reasons why a venture debt investment may fail. Some common reasons include: the company’s inability to generate enough revenue to cover its debt payments, unexpected market changes or disruptions, poor management decisions, and overreliance on debt financing instead of equity financing.
In some cases, venture debt lenders may also be too aggressive in their lending practices, leading to companies taking on too much debt and becoming overleveraged.
Can you provide examples of venture debt failures?
There have been many high-profile examples of venture debt failures over the years. Some notable examples include: the bankruptcy of solar panel manufacturer Solyndra, the collapse of online retailer Fab.com, and the bankruptcy of healthcare technology company Theranos.
In each of these cases, the companies took on significant amounts of debt but were unable to generate enough revenue to cover their debt payments or sustain their business models over the long term.
What can companies do to avoid venture debt failures?
To avoid venture debt failures, companies should focus on building sustainable business models that generate enough revenue to cover their debt payments and other expenses. Companies should also be cautious about taking on too much debt and should consider using a mix of equity and debt financing to fund their growth.
It’s also important for companies to have strong management teams in place and to be prepared for unexpected market changes or disruptions that could impact their business.
What should venture debt lenders do to minimize their risk of failure?
Venture debt lenders can minimize their risk of failure by conducting thorough due diligence on potential borrowers, carefully evaluating their business models and growth prospects, and structuring their loans in a way that minimizes the risk of default.
Lenders should also be cautious about taking on too much risk and should be prepared to work with borrowers to restructure their debt or provide other forms of support if they run into financial difficulties.
Top 6 Mistakes Startups Make When Raising Venture Debt
In conclusion, venture debt can be a useful tool for startups looking to fund their operations and growth. However, it is not without risk, and there have been some notable failures in the venture debt space. These failures can be attributed to a variety of factors, including over-leveraging, poor management, and market conditions.
One of the most notable venture debt failures was that of Homejoy, a home services startup that raised $38 million in venture capital and debt. Despite its early success, Homejoy ultimately failed due to a combination of internal issues and intense competition from other players in the market.
Another high-profile failure was that of Skully, a startup that raised over $11 million in venture debt to develop a smart motorcycle helmet. Skully ultimately failed due to mismanagement and a lack of focus on product development, which led to the company burning through its cash before delivering a viable product.
Overall, while venture debt can be a valuable source of funding, it is important for startups to carefully consider the risks and potential downsides before taking on debt. By learning from the failures of past startups, entrepreneurs can better position themselves for success in the venture debt space.
