Venture debt financing is an increasingly popular method of funding for startups and growing businesses. Although it may sound similar to traditional bank loans, venture debt has unique features that set it apart. One of these features is the repayment structure, which can be confusing for those new to the world of venture debt. In this article, we will explore how venture debt repayment works and what businesses should keep in mind when considering this type of financing.
How Does Venture Debt Repayment Work?
Venture debt is an alternative financing option for startups that are looking to raise capital without giving away equity. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically offered by specialized lenders who cater to the unique needs of startups. However, like any loan, venture debt must be repaid. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how venture debt repayment works.
1. Understanding Venture Debt
Venture debt is a form of debt financing that is often used by startups to bridge the gap between equity rounds or as a complement to equity financing. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically offered by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of startups. Venture debt is typically structured as a loan with interest and principal payments, just like any other loan.
When a startup takes on venture debt, they are essentially borrowing money with the expectation that they will be able to generate enough revenue to pay back the loan. The lender will typically require some form of collateral, such as accounts receivable or inventory, to secure the loan.
2. How Venture Debt Repayment Works
Venture debt repayment works much like any other loan. The borrower is required to make regular payments of principal and interest until the loan is fully paid off. The frequency of payments, the interest rate, and the term of the loan will vary depending on the lender and the specific terms of the loan agreement.
In most cases, venture debt repayment is structured as monthly payments of interest and principal. The interest rate on venture debt is typically higher than traditional bank loans due to the increased risk associated with lending to startups. However, the interest rate on venture debt is typically lower than the cost of equity financing.
3. Benefits of Venture Debt Repayment
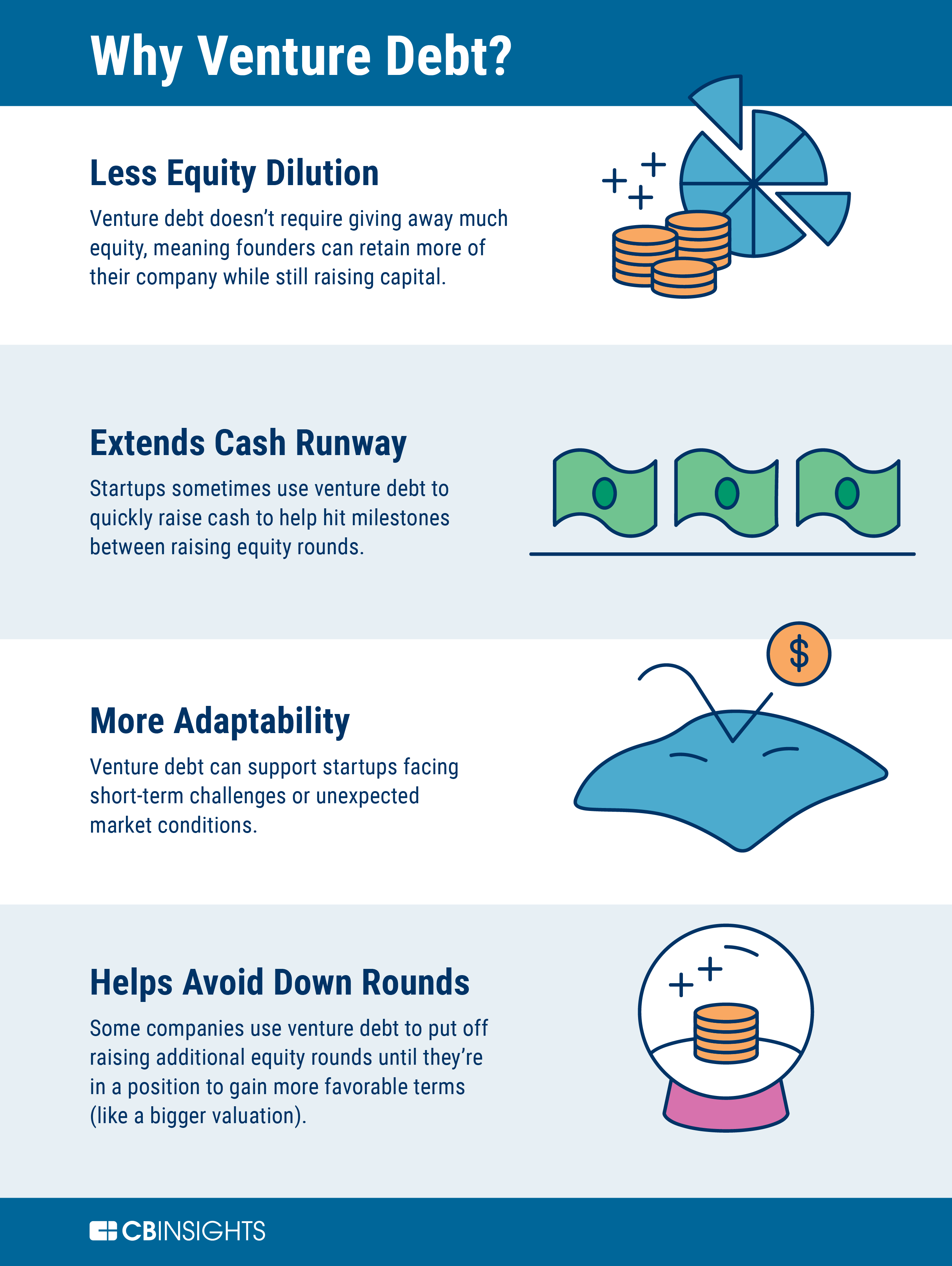
There are several benefits to using venture debt as a financing option for startups. First, venture debt allows startups to raise capital without giving away equity. This means that the founders can maintain control of the company and avoid dilution of their ownership stake. Second, venture debt is typically less expensive than equity financing, as the interest rate on venture debt is typically lower than the cost of equity financing. Finally, venture debt can be used to bridge the gap between equity rounds, allowing startups to continue to grow and scale their business.
4. Venture Debt vs. Traditional Bank Loans
Venture debt is different from traditional bank loans in several ways. First, venture debt lenders typically specialize in lending to startups and understand the unique needs of these companies. This means that they are more likely to be flexible in their lending terms and may be more willing to take on higher risk than traditional banks.
Second, venture debt is typically structured as a loan with interest and principal payments, just like any other loan. Traditional bank loans may have more complex repayment terms, such as balloon payments or variable interest rates.
5. Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
Venture debt is also different from equity financing in several ways. Equity financing involves selling ownership in the company in exchange for capital. This means that the founders will have less control over the company and may be subject to dilution of their ownership stake.
Venture debt, on the other hand, allows startups to raise capital without giving away equity. This means that the founders can maintain control of the company and avoid dilution of their ownership stake. Additionally, venture debt is typically less expensive than equity financing, as the interest rate on venture debt is typically lower than the cost of equity financing.
6. Risks of Venture Debt Repayment
While venture debt can be a useful financing option for startups, there are also some risks associated with this type of financing. First, venture debt is typically more expensive than traditional bank loans due to the increased risk associated with lending to startups. Second, if the startup is unable to generate enough revenue to repay the loan, the lender may be forced to take legal action to recover the collateral.
Finally, if the startup is unable to repay the loan, the lender may be able to take ownership of the collateral. This can be particularly problematic if the collateral is essential to the operation of the business.
7. How to Qualify for Venture Debt
Qualifying for venture debt can be challenging, as lenders typically have strict requirements for borrowers. To qualify for venture debt, startups will typically need to have a proven track record of revenue growth and profitability. Additionally, the startup will need to have a strong management team and a solid business plan.
Startups that are considering venture debt should be prepared to provide detailed financial information to the lender, including revenue projections, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. The lender will also typically require some form of collateral, such as accounts receivable or inventory, to secure the loan.
8. How to Find Venture Debt Lenders
Finding venture debt lenders can be challenging, as these lenders are typically specialized and may not be well-known in the startup community. However, there are several resources available to startups that are looking for venture debt financing.
One option is to work with a venture debt broker, who can help startups identify potential lenders and negotiate loan terms. Another option is to attend industry conferences and networking events, where startups can meet with venture debt lenders and pitch their business.
9. Conclusion
Venture debt can be a useful financing option for startups that are looking to raise capital without giving away equity. While venture debt repayment works much like any other loan, there are some risks associated with this type of financing. Startups that are considering venture debt should be prepared to provide detailed financial information to the lender and have a solid business plan.
10. Additional Resources
For startups that are interested in learning more about venture debt, there are several resources available. The National Venture Capital Association (NVCA) provides information on the venture debt industry, including a list of venture debt lenders. The NVCA also hosts an annual venture debt summit, where startups can learn more about this type of financing. Additionally, startups can work with a venture debt broker, who can help them identify potential lenders and negotiate loan terms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing offered to startups and other high-growth companies that have already raised equity financing. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders and is often secured by the company’s assets, including intellectual property, equipment, and accounts receivable.
Venture debt is often used to extend the runway of a startup or to fund a specific project or acquisition. It can be a useful source of financing for companies that need capital but do not want to dilute their ownership by raising additional equity.
How does venture debt differ from traditional bank loans?
Venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of startups and high-growth companies. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is often secured by the company’s assets, including intellectual property, equipment, and accounts receivable.
In addition, venture debt lenders often provide more flexible repayment terms than traditional banks. For example, they may offer interest-only payments for a period of time or allow the borrower to make principal payments on a schedule that aligns with the company’s cash flow.
How does venture debt repayment work?
Venture debt repayment typically involves making regular payments of principal and interest over a set period of time, often three to five years. The terms of the loan agreement will specify the payment schedule and the interest rate, which is typically higher than what is offered by traditional bank loans.
In some cases, venture debt lenders may offer more flexible repayment terms, such as interest-only payments for a period of time or the ability to make principal payments on a schedule that aligns with the company’s cash flow.
What are the advantages of venture debt?
Venture debt can be a useful source of financing for startups and high-growth companies that need capital but do not want to dilute their ownership by raising additional equity. It can also be a useful tool for extending the runway of a startup or funding a specific project or acquisition.
In addition, venture debt lenders often provide more flexible repayment terms than traditional banks, which can help companies manage their cash flow and avoid dilution.
What are the risks of venture debt?
Venture debt can be a risky form of financing for startups and high-growth companies. Because the interest rates are typically higher than what is offered by traditional bank loans, the cost of capital can be substantial.
In addition, venture debt lenders often require the borrower to provide collateral, such as intellectual property, equipment, or accounts receivable, which can be risky for the borrower if the company is unable to repay the loan. Finally, if the company is unable to meet its repayment obligations, the lender may have the right to seize the collateral and liquidate it to recover the debt.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, venture debt repayment works differently from traditional bank loans. It is a financing option that is available to startups that have already received equity funding. Through venture debt, these startups can access additional capital without diluting their ownership stake. Repayment of venture debt typically involves monthly interest payments and a balloon payment at the end of the loan term.
While venture debt can be a useful tool for startups looking to accelerate growth, it is important to carefully consider the terms of the loan. Startups should ensure they have a clear plan for how they will generate the cash flow needed to make the monthly interest payments and repay the principal. Additionally, startups should be aware of any covenants that may be included in the loan agreement, which could restrict their ability to take on additional debt or make strategic decisions.
Overall, venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups that have already received equity funding. By understanding how venture debt repayment works and carefully considering the terms of the loan, startups can access the capital they need to fuel growth while minimizing dilution of their ownership stake.
