Venture debt financing is becoming increasingly popular for startups looking for alternative ways to raise capital. While it may not be as well-known as traditional equity financing, it can be a valuable tool for companies that want to maintain control over their business and avoid diluting their ownership stake. But what exactly does a venture debt agreement look like, and what should startups know before signing on the dotted line?
In this article, we’ll explore the key components of a venture debt agreement, including interest rates, covenants, and repayment terms. We’ll also discuss some of the benefits and risks of this type of financing, and offer tips for startups looking to secure venture debt funding. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, understanding the ins and outs of venture debt can help you make informed decisions about your business’s financial future.
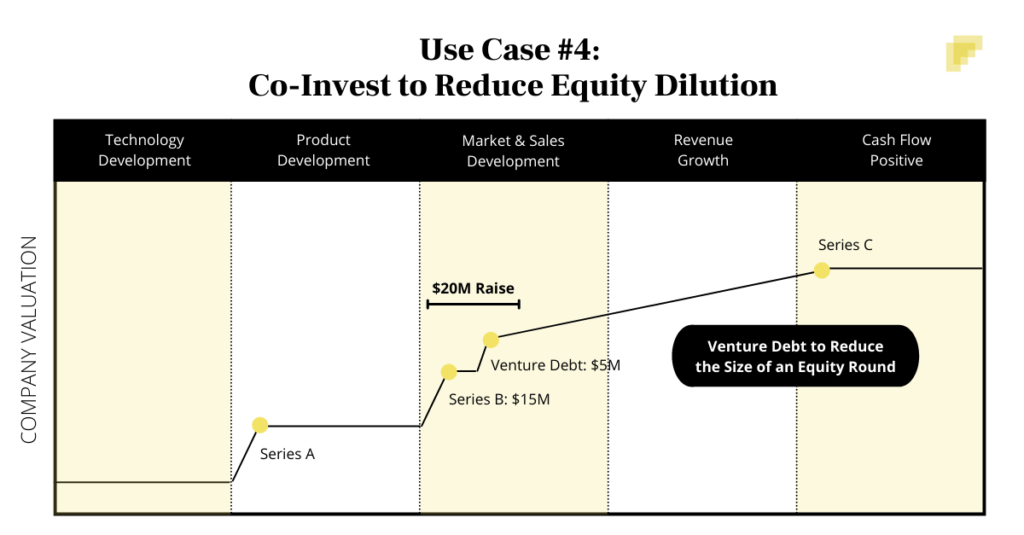
How Does a Venture Debt Agreement Look?
When startups seek funding, venture capital comes to mind as the most common option. However, there’s another type of financing that startups can consider: venture debt. Venture debt offers a way for startups to get funding without giving up equity. But what does a venture debt agreement look like? Let’s take a closer look.
1. Overview of Venture Debt
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that provides funding to startups. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is tailored to meet the needs of startups, which often have limited operating history and revenue. Venture debt typically has higher interest rates than traditional loans to compensate for the higher risk involved.
Venture debt can take various forms, such as term loans, lines of credit, or convertible debt. The terms and conditions of venture debt agreements vary depending on the lender and the startup’s circumstances.
2. Terms of a Venture Debt Agreement
The terms of a venture debt agreement usually include the amount of funding, interest rate, repayment schedule, and covenants. The amount of funding depends on the startup’s needs and the lender’s assessment of the startup’s ability to repay the debt.
Interest rates on venture debt are typically higher than traditional loans. Startups should carefully consider the cost of the debt before accepting the terms of the agreement. Repayment schedules can vary depending on the lender and the type of debt.
Covenants are conditions that the startup must meet to maintain the debt agreement. Covenants can include financial metrics, such as revenue or cash flow, or operational metrics, such as hiring or product development milestones.
3. Benefits of Venture Debt
Venture debt has several benefits for startups. First, it provides funding without diluting equity. Startups can retain ownership and control over their business while still getting the funding they need to grow.
Second, venture debt can provide additional runway for startups. Startups can use the funding to extend their cash runway and focus on growth without worrying about running out of money.
Third, venture debt can be a useful tool for startups that have already raised equity funding. Venture debt can help bridge the gap between equity rounds and provide additional funding to support growth.
4. Differences Between Venture Debt and Equity
Venture debt and equity are two different types of financing that startups can consider. Equity financing involves selling shares of the company in exchange for funding, while venture debt involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest.
One of the main differences between venture debt and equity is ownership. With equity financing, investors become owners of the company and have a say in how the company is run. With venture debt, the startup retains ownership and control over the business.
Another difference is the risk involved. With equity financing, investors take on the risk of the investment. If the company fails, the investors lose their investment. With venture debt, the risk falls on the startup. If the company fails, the debt must still be repaid.
5. When to Consider Venture Debt
Venture debt can be a good option for startups that have already raised equity funding and want to extend their cash runway. It can also be a good option for startups that have a clear path to profitability but need additional funding to get there.
Startups should carefully consider the cost of venture debt before accepting the terms of the agreement. They should also weigh the benefits of venture debt against the benefits of equity financing to determine which option is best for their business.
6. Venture Debt vs. Traditional Loans
Venture debt differs from traditional bank loans in several ways. Traditional bank loans are typically secured by collateral, such as property or equipment, and have lower interest rates than venture debt.
Venture debt, on the other hand, is unsecured and has higher interest rates to compensate for the higher risk involved. It also typically has more flexibility in terms of repayment schedules and covenants.
7. Venture Debt vs. Convertible Debt
Convertible debt is another type of debt financing that startups can consider. Convertible debt is a loan that can be converted into equity at a later date, typically when the startup raises its next equity round.
The main difference between convertible debt and venture debt is the conversion option. With convertible debt, the lender has the option to convert the debt into equity, while with venture debt, the lender is only entitled to repayment of the debt with interest.
8. Who Provides Venture Debt
Several types of lenders provide venture debt, including banks, specialty finance companies, and venture debt funds. Each type of lender has its own criteria for lending and its own terms and conditions.
Startups should carefully consider the reputation and track record of the lender before accepting venture debt. They should also ensure that the terms of the agreement are favorable and meet their needs.
9. Conclusion
Venture debt can be a useful tool for startups that need funding without giving up equity. Venture debt agreements typically include the amount of funding, interest rate, repayment schedule, and covenants.
Startups should carefully consider the cost of venture debt before accepting the terms of the agreement. They should also weigh the benefits of venture debt against the benefits of equity financing to determine which option is best for their business.
10. References
– “What Is Venture Debt?” by Investopedia
– “The Pros and Cons of Venture Debt” by Entrepreneur
– “Venture Debt: What It Is, When to Use It, and How to Get It” by Forbes
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about venture debt agreements:
What is a venture debt agreement?
A venture debt agreement is a loan agreement between a venture debt provider and a startup company. Unlike traditional debt financing, venture debt usually comes with less restrictive terms and higher interest rates to compensate for the higher risk involved. These agreements may also include warrants or equity options as additional compensation for the lender.
The terms of a venture debt agreement will vary depending on the lender and the needs of the startup, but they often include details such as the loan amount, interest rate, repayment schedule, and any collateral or guarantees required.
What are the benefits of a venture debt agreement?
One of the main benefits of a venture debt agreement is that it allows startups to raise additional capital without diluting their equity. In other words, the company can borrow money without giving up ownership or control to investors. This can be especially attractive for companies that are not yet profitable or are not ready for a traditional equity financing round.
Another benefit is that venture debt agreements can provide startups with more flexibility than other types of financing. For example, the repayment schedule may be structured to align with the company’s cash flow needs, and the lender may be more willing to work with the company if it experiences temporary setbacks or delays in reaching its milestones.
What are the risks of a venture debt agreement?
As with any type of financing, there are risks involved with venture debt agreements. One potential risk is that the interest rates may be higher than other types of debt financing, which can make it more expensive for the company to borrow money.
Another risk is that the lender may require collateral or guarantees, which could put the company’s assets at risk if it is unable to repay the loan. Additionally, if the company is unable to meet its repayment obligations, it could damage its credit score and make it more difficult to secure financing in the future.
How can I find a venture debt provider?
There are many venture debt providers in the market, ranging from banks and specialty finance companies to venture debt funds. One way to find potential lenders is to ask for recommendations from other entrepreneurs or investors in your network.
You can also use online resources such as venture debt databases or industry publications to identify potential lenders. Once you have a list of potential lenders, you should carefully review their terms and do your due diligence to ensure that they are a good fit for your company.
What should I consider before signing a venture debt agreement?
Before signing a venture debt agreement, it is important to carefully review the terms and understand the implications of the loan. You should consider factors such as the interest rate, repayment schedule, collateral requirements, and any warrants or equity options included in the agreement.
You should also consider the potential risks and benefits of the loan, as well as the lender’s reputation and track record. It may be helpful to consult with a lawyer or financial advisor to ensure that you fully understand the terms of the agreement and the potential implications for your business.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, a venture debt agreement is a valuable tool for startups looking to raise capital without sacrificing equity. The agreement typically includes a loan with a fixed interest rate, as well as warrants that allow the lender to purchase equity in the company at a later date.
While the terms of a venture debt agreement can vary, it is important for both the borrower and lender to carefully consider the terms and negotiate a fair deal. Startups should be aware of the potential risks, such as high interest rates and the potential dilution of equity, and ensure that they have a solid plan for repayment.
Despite these risks, venture debt can be a useful financing option for startups that need capital to grow and scale their business. By understanding how a venture debt agreement works and what to look for in a lender, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions about their financing options and set themselves up for success in the long run.
