Venture debt has become an increasingly popular financing option for startups looking to grow their business. However, it’s important to note that this type of debt comes with its own set of risks. In this article, we will delve into the reasons why venture debt is considered a risky form of financing and what entrepreneurs need to be aware of before choosing this option.
Why Venture Debt is Considered Risky: Understanding the Risks Involved
1. High Interest Rates
Venture debt is a type of financing that is typically offered to startups and other early-stage companies that are not yet profitable. While it can be an attractive option for companies that need cash quickly, it also comes with some significant risks.
One of the biggest risks associated with venture debt is the high interest rates that are often charged. Because these loans are considered to be high-risk investments, lenders typically charge much higher interest rates than they would for more traditional loans. This can make it difficult for companies to make their payments, and can even lead to default.
To mitigate this risk, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate their financial situation and ensure that they will be able to make their payments on time.
2. Limited Cash Flow
Another major risk associated with venture debt is the limited cash flow that is often available to companies. Because these loans are typically short-term, companies may find themselves struggling to make ends meet as they wait for their next round of funding.
To address this risk, it is important for companies to carefully manage their cash flow and ensure that they have enough money on hand to cover their expenses in the short term.
3. Uncertainty of Future Funding
Venture debt also comes with a significant amount of uncertainty when it comes to future funding. Because these loans are often used to bridge the gap between rounds of fundraising, it can be difficult for companies to predict when they will be able to secure additional funding.
To mitigate this risk, it is important for companies to maintain good relationships with their investors and to build a strong reputation in the industry. This can help to increase the likelihood of future funding and reduce the risk of default.
4. Lack of Collateral
Unlike traditional loans, venture debt often does not require collateral. This means that lenders are taking a significant risk by lending money to companies that may not have any assets to back up the loan.
To address this risk, it is important for companies to have a solid business plan in place and to demonstrate a strong track record of success. This can help to reassure lenders that they are making a good investment and reduce the risk of default.
5. Limited Exit Opportunities
Another risk associated with venture debt is the limited exit opportunities that are available to companies. Because these loans are often used to fund early-stage companies, there may not be many options for companies to exit the investment and repay their lenders.
To mitigate this risk, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate their exit options and to ensure that they have a solid plan in place for repaying their debt.
6. Lack of Control
Venture debt also comes with a lack of control for companies. Because lenders are taking a significant risk by lending money to early-stage companies, they may require a significant amount of control over the company’s operations in order to mitigate their risk.
To address this risk, it is important for companies to carefully negotiate the terms of their loan agreements and to ensure that they are comfortable with the level of control that lenders may require.
7. Limited Flexibility
Another risk associated with venture debt is the limited flexibility that is often available to companies. Because these loans are typically short-term, companies may find themselves locked into a payment schedule that does not allow for much flexibility.
To mitigate this risk, it is important for companies to carefully negotiate the terms of their loan agreements and to ensure that they have some flexibility when it comes to making their payments.
8. Limited Investor Interest
Venture debt can also be risky because it may not be as attractive to investors as other forms of financing. Because these loans are often considered to be high-risk investments, investors may be hesitant to invest in companies that have taken on significant amounts of debt.
To address this risk, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate their funding options and to consider all available options before deciding to take on venture debt.
9. Limited Growth Potential
Another risk associated with venture debt is the limited growth potential that is often available to companies. Because these loans are typically used to bridge the gap between funding rounds, companies may find themselves limited in terms of their ability to grow and expand.
To mitigate this risk, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate their funding options and to ensure that they have a solid plan in place for future growth.
10. Higher Risk of Default
Finally, venture debt comes with a higher risk of default than other forms of financing. Because these loans are considered to be high-risk investments, companies may find themselves struggling to make their payments and may ultimately default on their loans.
To address this risk, it is important for companies to carefully evaluate their financial situation and to ensure that they are comfortable taking on the additional risk associated with venture debt. It is also important for companies to maintain good relationships with their lenders and to work closely with them to address any potential issues that may arise.
In conclusion, while venture debt can be an attractive financing option for companies that need cash quickly, it also comes with significant risks. By carefully evaluating their financial situation, negotiating the terms of their loan agreements, and maintaining good relationships with their lenders, companies can mitigate these risks and successfully navigate the world of venture debt financing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about venture debt and the risks associated with it:
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is typically offered to startup companies that have already raised some equity capital. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is often structured as a line of credit or a term loan and is secured by the company’s assets. It is often used to bridge the gap between equity rounds or to finance specific projects.
What are the benefits of venture debt?
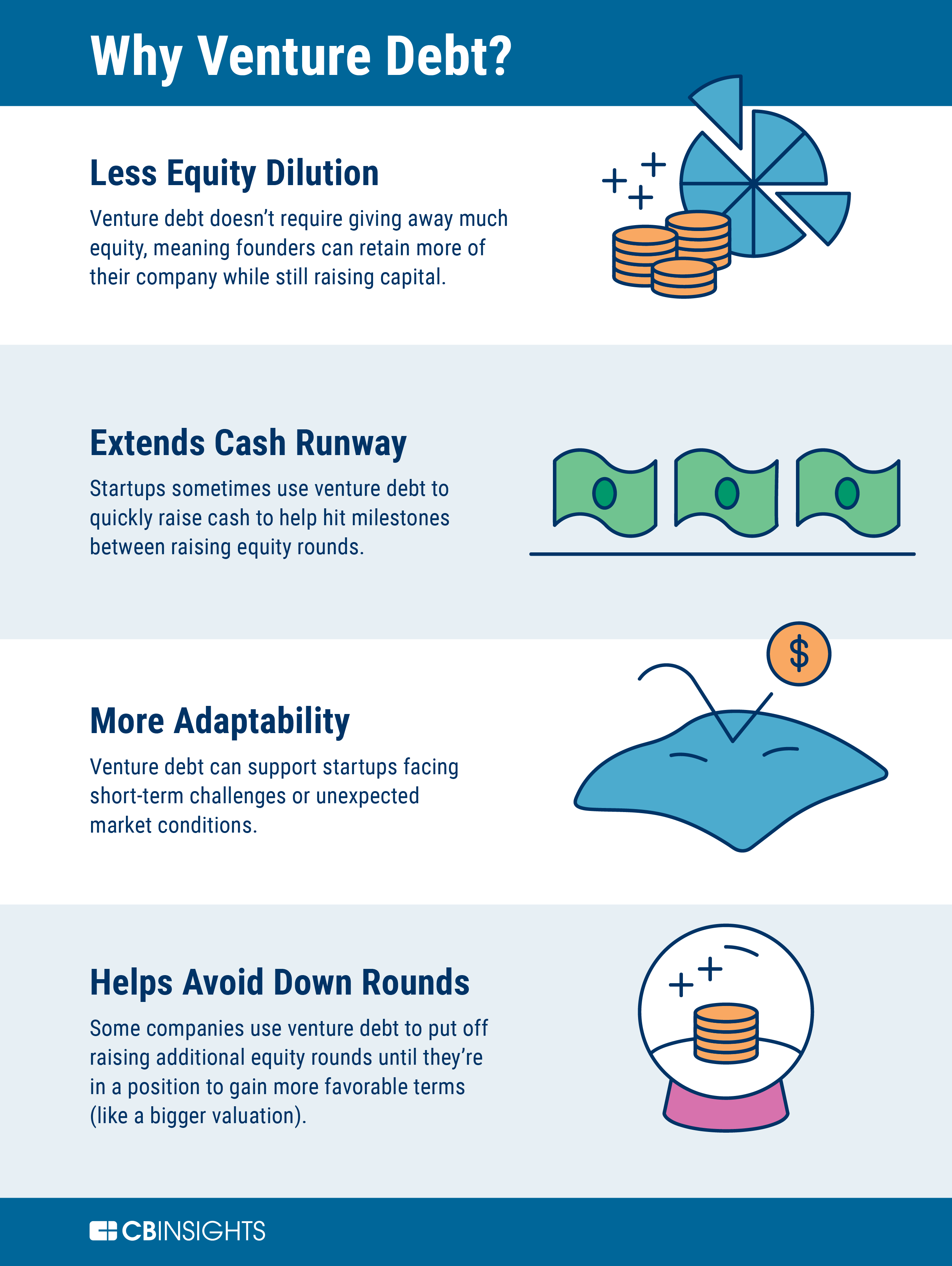
Venture debt can provide startups with additional capital without diluting the ownership of existing shareholders. It can also be a less expensive form of financing compared to equity, as the interest rates are typically lower. Additionally, venture debt lenders may provide valuable industry expertise and networking opportunities to the startups they invest in.
How is venture debt different from traditional debt?
Venture debt is different from traditional debt in several ways. Firstly, traditional debt is usually offered to established companies with a proven track record of generating revenue and profits. Venture debt, on the other hand, is offered to startups that have yet to establish a financial track record. Additionally, traditional debt is usually secured by the company’s assets, whereas venture debt may be secured by a combination of assets and equity. Finally, traditional debt typically has lower interest rates and longer repayment terms compared to venture debt.
What are the risks associated with venture debt?
Venture debt is considered risky because it is typically offered to startups that have yet to establish a financial track record. This means that the lender is taking on a higher level of risk compared to traditional lenders. Additionally, venture debt lenders may not have the same level of collateral as traditional lenders, which means that they may not be able to recoup their investment if the startup fails. Finally, venture debt is often structured with covenants and other restrictions that can limit the startup’s ability to operate and grow.
How can startups manage the risks associated with venture debt?
Startups can manage the risks associated with venture debt by thoroughly researching and vetting potential lenders. They should also carefully consider the terms and conditions of the debt before accepting it. Additionally, startups should only take on debt that they can realistically repay, and should have a plan in place in case they are unable to meet their obligations. Finally, startups should communicate regularly with their lenders and be transparent about their financial situation.
GRC Chat #56 – Venture Debt Explained and De-Risked with Zack Ellison
In conclusion, venture debt is considered risky for several reasons. Firstly, it is a form of debt financing that is typically offered to startups and early-stage companies, which are inherently risky investments. These companies often have limited operating histories, unproven business models, and uncertain revenue streams. As a result, lenders may charge higher interest rates and require stricter repayment terms to compensate for the added risk.
Secondly, venture debt is often secured by the company’s assets, including intellectual property and equity. This means that if the company fails to repay the loan, the lender may have the right to seize these assets to recoup its losses. This can be particularly problematic for startups and early-stage companies, which may not have many tangible assets to offer as collateral.
Finally, venture debt is typically structured as a short-term loan with a balloon payment due at the end of the term. This means that the borrower must repay the entire loan amount, plus interest, at once. If the borrower is unable to do so, they may be forced to refinance the debt or seek additional financing, which can be difficult for companies that are already struggling.
Overall, while venture debt can be a useful tool for startups and early-stage companies looking to raise capital, it is important to weigh the risks and benefits carefully. Companies should consider their ability to repay the loan, the impact on their equity and intellectual property, and the potential for future financing needs before deciding whether venture debt is the right choice for them.
