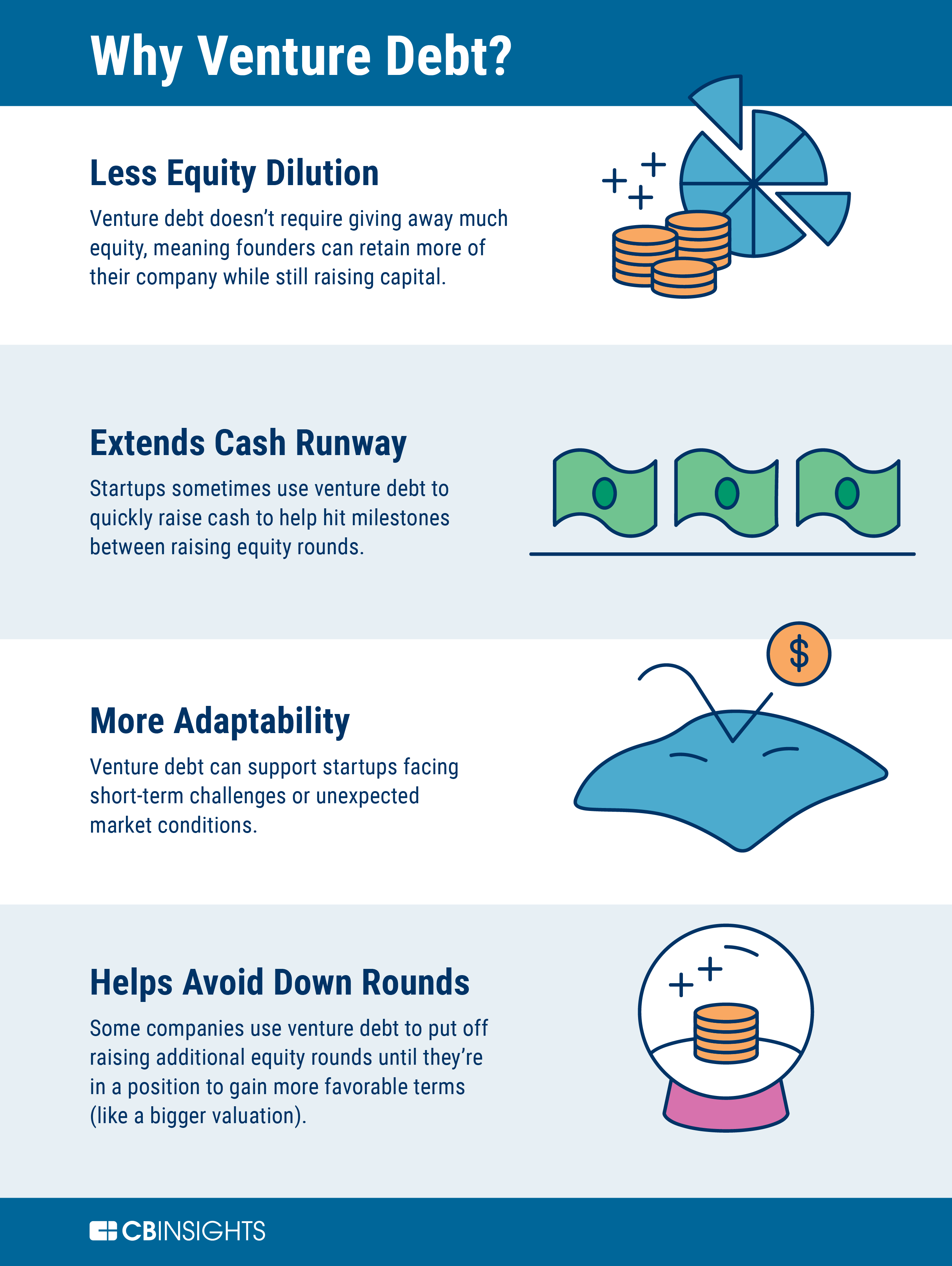
Venture debt has become an increasingly popular financing option for startups looking to grow their business without diluting equity. However, one aspect of venture debt that often confuses entrepreneurs is the inclusion of warrants. So, why exactly does venture debt include warrants?
Warrants are essentially a form of equity option that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to purchase equity in the issuing company at a predetermined price. In the context of venture debt, warrants are often included as a way to provide additional upside potential for the lender while also mitigating their risk.
Why Does Venture Debt Include Warrants?
Venture debt is a form of financing that is becoming increasingly popular among startups. It is a debt financing option that provides cash to a company in exchange for the promise of repayment with interest. In addition, many venture debt agreements include warrants. So, why does venture debt include warrants? In this article, we will explore the reasons behind this trend.
What are Warrants?
A warrant is a financial instrument that gives the holder the right to purchase a company’s stock at a specific price within a certain time frame. Warrants are often used as a sweetener in debt financing agreements. They are similar to stock options, but they are issued by the company and not traded on an exchange. Warrants can be valuable if the company’s stock price increases because they allow the holder to purchase the stock at a lower price.
Warrants are typically used in venture debt agreements to compensate the lender for taking on additional risk. Venture debt is riskier than traditional debt financing because startups are often not profitable and have a higher chance of failure. By including warrants, the lender has the potential to earn a greater return on their investment if the startup is successful.
Benefits of Including Warrants in Venture Debt Agreements
There are several benefits to including warrants in venture debt agreements. First, warrants can provide additional upside potential for the lender. If the company’s stock price increases, the lender can exercise the warrants and purchase stock at a lower price, increasing their return on investment.
Second, warrants can be used to incentivize the lender to provide the financing. Startups often have difficulty securing traditional debt financing because they are not yet profitable. By offering warrants, the lender is more likely to provide the financing because they have the potential for a greater return on investment.
Finally, warrants can be used to align the interests of the lender and the borrower. If the borrower is successful, the lender’s investment will be worth more because of the warrants. This can incentivize the lender to provide additional financing in the future.
How Do Warrants Impact the Cost of Capital?
Including warrants in a venture debt agreement can impact the cost of capital for the borrower. Warrants are a form of equity, so they dilute the ownership of the existing shareholders. This can make it more difficult for the company to raise additional equity financing in the future because the existing shareholders will own a smaller percentage of the company.
However, the impact of warrants on the cost of capital can be positive if the company is successful. If the company’s stock price increases, the warrants will be exercised, and the lender will purchase stock at a lower price. This increases the lender’s return on investment and can make it easier for the company to secure additional financing in the future.
Warrants vs. Convertible Notes
Warrants are often compared to convertible notes because they are both types of debt financing that can be converted into equity. However, there are some key differences between the two.
Convertible notes are a type of debt financing that can be converted into equity at a specific point in the future. They do not give the holder the right to purchase stock at a specific price like warrants do. In addition, convertible notes typically have a lower interest rate than venture debt agreements that include warrants.
Warrants, on the other hand, give the holder the right to purchase stock at a specific price within a certain time frame. They are often used in conjunction with venture debt agreements to provide additional upside potential for the lender.
Conclusion
In conclusion, warrants are becoming increasingly popular in venture debt agreements because they provide additional upside potential for the lender. They can be used to incentivize the lender to provide the financing and align the interests of the lender and the borrower. While warrants can impact the cost of capital for the borrower, they can also be a positive if the company is successful. Overall, including warrants in venture debt agreements can be a win-win for both the lender and the borrower.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are venture debt warrants?
Venture debt warrants are a type of financial instrument that gives the lender the option to purchase equity in a company at a future date and at a predetermined price. They are often included in venture debt deals as a way for lenders to potentially increase their returns on investment.
These warrants are typically issued alongside the debt and can be exercised if the borrower does not repay the loan or if certain performance metrics are met.
How do venture debt warrants benefit lenders?
Venture debt lenders often include warrants in their deals because they provide the potential for additional returns on investment beyond the interest paid on the debt. If the company performs well and the stock price increases, the lender can exercise the warrants and purchase equity at a lower price, effectively increasing their return on investment.
Warrants also provide lenders with some protection in case the company does not perform as expected. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can exercise the warrants and potentially recoup some of their losses by selling the equity at a higher price.
Why do companies agree to include venture debt warrants?
For companies, venture debt warrants can be an attractive form of financing because they often come with lower interest rates than traditional loans. Additionally, the warrants provide lenders with an incentive to work with the company to help it grow and succeed, as this will increase the value of the equity that the lender may eventually purchase.
However, it’s important for companies to carefully consider the potential dilution of their equity that may result from the issuance of warrants, as well as the potential impact on future funding rounds and valuations.
What are the risks associated with venture debt warrants?
As with any investment, venture debt warrants come with some level of risk. If the company does not perform as expected, the value of the equity may decrease, and the lender may not exercise the warrants. Additionally, if the company experiences financial difficulties or goes bankrupt, the warrants may become worthless.
There is also the risk of dilution for existing shareholders if the lender exercises the warrants and purchases equity in the company at a lower price than its current valuation.
How can companies mitigate the risks associated with venture debt warrants?
To mitigate the risks associated with venture debt warrants, companies can carefully consider the terms of the warrant agreement and negotiate for favorable terms. This may include setting a higher exercise price or including provisions that limit the number of warrants that can be exercised at any one time.
Companies can also work to ensure that they have a solid business plan and that they are meeting their performance metrics, as this will increase the likelihood that the lender will exercise the warrants and purchase equity at a higher price.
Venture Debt: Warrant Coverage Upfront or On Usage
In conclusion, venture debt is a popular financing option for startups that need additional capital to fuel their growth. One of the unique features of venture debt is the inclusion of warrants. These warrants are essentially options that give the lender the right to purchase shares of the company at a predetermined price in the future.
The inclusion of warrants in venture debt serves a few important purposes. First, it helps to reduce the overall cost of capital for the borrower. Since the lender has the potential to benefit from the future success of the company, they may be willing to offer more favorable loan terms. Second, warrants give the lender a stronger incentive to work with the borrower to help them succeed. If the company does well and the stock price increases, the lender stands to benefit as well.
Overall, the inclusion of warrants in venture debt is a unique and important feature of this type of financing. While it may not be right for every company, it can be a valuable tool for startups looking to raise capital and grow their business. By understanding how warrants work and what they can offer, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions about their financing options and set themselves up for long-term success.
