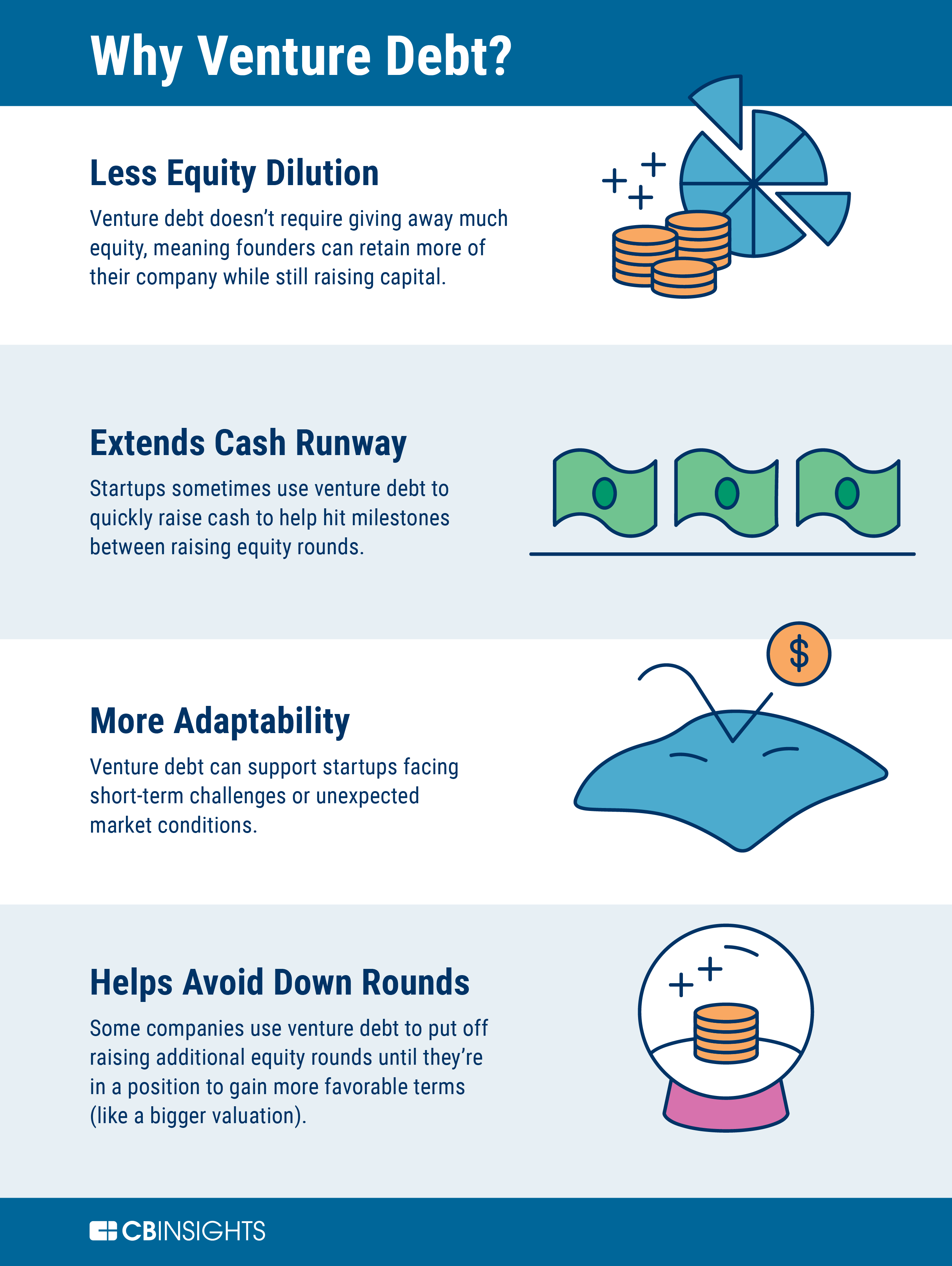
Venture debt is a type of financing that has become increasingly popular among startups and emerging businesses. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt allows companies to access capital without giving up equity in their company. But why do lenders take on the risk of offering venture debt?
The answer lies in the potential for high returns. Lenders are willing to take on more risk with venture debt because they have the opportunity to earn a higher interest rate than they would with traditional loans. Additionally, if the company does well and eventually goes public or gets acquired, lenders may also have the opportunity to convert their debt into equity, potentially earning even greater returns.
Why Do Lenders Take on Venture Debt Risk?
Venture debt is a type of financing that is provided to startups and high-growth companies, usually in combination with equity financing. It is a form of debt financing that is considered to be higher risk than traditional bank loans, but also offers potential for higher returns. In this article, we will explore why lenders take on venture debt risk.
1. High-Return Potential
One of the main reasons why lenders take on venture debt risk is the potential for high returns. Unlike traditional debt financing, venture debt comes with higher interest rates and other fees. In addition, lenders often receive warrants or other equity incentives as part of the loan agreement. These equity incentives can provide significant upside potential if the company is successful.
Moreover, venture debt is typically provided to companies that are expected to grow rapidly and eventually go public or be acquired. If the company is successful, the lender can receive a significant return on their investment.
2. Diversification of Portfolio
Lenders often take on venture debt risk as a way to diversify their portfolio. Venture debt is typically provided to companies that are in emerging industries or have disruptive business models. These companies may not fit the traditional lending criteria of banks or other financial institutions.
By investing in these companies, lenders can diversify their portfolio and potentially earn higher returns than they would with traditional investments. This can help mitigate the risk of losses in other areas of their portfolio.
3. Mitigation of Equity Risk
Lenders that provide venture debt can also mitigate their equity risk by providing debt financing instead of equity financing. Equity financing involves giving up ownership in the company, which can be risky if the company does not perform as expected. With venture debt, lenders do not give up ownership in the company and have a higher priority claim on the company’s assets in the event of a default.
This can be particularly attractive to lenders that want exposure to high-growth companies but do not want to take on the full equity risk.
4. Access to High-Growth Companies
Lenders that provide venture debt can also gain access to high-growth companies that may not be available through traditional lending channels. These companies are often in emerging industries or have innovative business models that traditional lenders may not understand or be willing to finance.
By providing venture debt, lenders can gain access to these companies and potentially benefit from their growth.
5. Competitive Advantage
Lenders that provide venture debt can also gain a competitive advantage over other lenders that do not offer this type of financing. This can be particularly attractive in industries where there is a lot of competition for lending opportunities.
By offering venture debt, lenders can differentiate themselves from other lenders and potentially attract more borrowers.
6. Relationship Building
Lenders that provide venture debt can also build relationships with high-growth companies that may be valuable in the future. These relationships can lead to future lending opportunities or even equity investments.
By building relationships with these companies early on, lenders can position themselves for future growth opportunities.
7. Potential for Referrals
Lenders that provide venture debt can also benefit from referrals from their portfolio companies. Successful startups and high-growth companies often have extensive networks of contacts and may refer other companies to the lender.
This can lead to a steady stream of new lending opportunities and potential for future growth.
8. Risk Management
Lenders that provide venture debt can also manage their risk by conducting extensive due diligence on the companies they lend to. This includes analyzing the company’s financial statements, business model, management team, and market opportunity.
By conducting thorough due diligence, lenders can identify potential risks and mitigate them before providing financing.
9. Flexibility
Venture debt offers greater flexibility than traditional bank loans. Lenders can structure venture debt financing in a way that meets the needs of the borrower. This can include flexible repayment terms, lower interest rates, and other customized features.
By offering flexible financing options, lenders can attract more borrowers and potentially earn higher returns.
10. Potential for Repeat Business
Finally, lenders that provide venture debt can benefit from repeat business from successful portfolio companies. If a company is successful and requires additional financing in the future, the lender that provided the initial venture debt financing may be well-positioned to provide additional funding.
This can lead to a steady stream of repeat business and potential for long-term growth.
In conclusion, lenders take on venture debt risk for a variety of reasons. These include the potential for high returns, diversification of portfolio, mitigation of equity risk, access to high-growth companies, competitive advantage, relationship building, potential for referrals, risk management, flexibility, and potential for repeat business. However, it is important to note that venture debt is a higher risk form of financing and requires extensive due diligence and risk management to be successful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a form of debt financing provided to early-stage and growth companies that have limited operating history, cash flow, or collateral. It is typically used by companies that have already raised equity funding and need additional capital to support their growth plans.
Venture debt is usually provided by specialized lenders who understand the risks and opportunities associated with investing in startups. The terms of venture debt are often more flexible than traditional debt financing, and the lenders may also receive equity or warrants as part of the deal.
How is venture debt different from equity financing?
Venture debt is different from equity financing in several ways. First, venture debt is a loan that must be repaid with interest, while equity financing involves selling a portion of the company to investors in exchange for funding. Second, venture debt does not dilute the ownership of the company, while equity financing does. Third, venture debt is typically less expensive than equity financing, but it also involves more risk for the lender.
Companies may choose to use venture debt instead of equity financing if they want to maintain control over their company and avoid diluting their ownership. However, venture debt may not be suitable for all companies, and it is important to understand the risks and costs involved.
What are the benefits of venture debt for lenders?
Venture debt can be an attractive option for lenders who are looking for higher returns than traditional debt financing. The interest rates on venture debt are typically higher than those on traditional loans, and lenders may also receive equity or warrants as part of the deal. Additionally, venture debt is less risky than equity financing, as the lender has a claim on the company’s assets in the event of default.
Venture debt can also be a way for lenders to establish relationships with promising startups and potentially earn a return on their investment if the company is successful. However, venture debt also involves more risk than traditional debt financing, and lenders should carefully assess the creditworthiness and growth potential of the company before making a loan.
What are the risks of venture debt for lenders?
Venture debt involves more risk than traditional debt financing, as the companies that seek venture debt often have limited operating history, cash flow, or collateral. This makes it more difficult to assess the creditworthiness of the borrower and increases the likelihood of default. Additionally, venture debt is typically unsecured, which means that the lender may not have collateral to recover in the event of default.
Furthermore, venture debt is often provided to companies that are already highly leveraged, which means that the lender may be in a subordinate position to other creditors in the event of bankruptcy. This increases the risk of loss for the lender.
How do lenders manage the risks of venture debt?
Lenders manage the risks of venture debt by carefully assessing the creditworthiness and growth potential of the borrower before making a loan. This includes analyzing the company’s financial statements, business plan, management team, and market opportunities. Lenders may also require collateral or personal guarantees from the borrower to mitigate the risk of default.
Additionally, lenders may structure the loan with covenants and other protections that give them more control over the borrower’s operations and financial management. This can include restrictions on the use of funds, limits on capital expenditures, and requirements for regular financial reporting. By taking these steps, lenders can reduce the risk of default and improve the chances of a successful outcome for both the borrower and the lender.
GRC Chat #56 – Venture Debt Explained and De-Risked with Zack Ellison
In conclusion, lenders take on venture debt risk for a variety of reasons. Firstly, venture debt can be a lucrative source of revenue for lenders. Lending to high-growth companies can yield high returns, and venture debt can be a way to diversify a lender’s portfolio. Additionally, lenders may be attracted to venture debt because of the potential for equity upside in the event of a successful exit.
Secondly, venture debt can provide a way for companies to access capital without diluting their ownership. This can be particularly appealing for founders who are hesitant to give up equity in their company. By taking on debt instead, companies can maintain more control over their business while still accessing the capital they need to grow.
Finally, venture debt can be a way for lenders to establish relationships with promising startups. By providing capital early on, lenders can build trust and credibility with founders, potentially leading to more business down the line. For lenders who specialize in venture debt, this can be a valuable way to establish themselves as a go-to source of capital for startups.
Overall, while venture debt does come with risk, there are many reasons why lenders are willing to take on that risk. Whether it’s for the potential for high returns, the opportunity to build relationships with promising startups, or the appeal of non-dilutive capital for founders, venture debt can be a valuable tool for both lenders and borrowers.
