Venture debt can be a valuable tool for startup companies looking to raise capital without giving up equity. However, it’s important to understand when this type of debt becomes due in order to manage cash flow effectively and avoid default.
Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt typically has shorter repayment terms and may be due within a few years. This means that startups need to have a solid plan in place to generate revenue and pay back the debt before the due date. In this article, we’ll explore the factors that determine when venture debt becomes due and what startups should consider when taking on this type of financing.
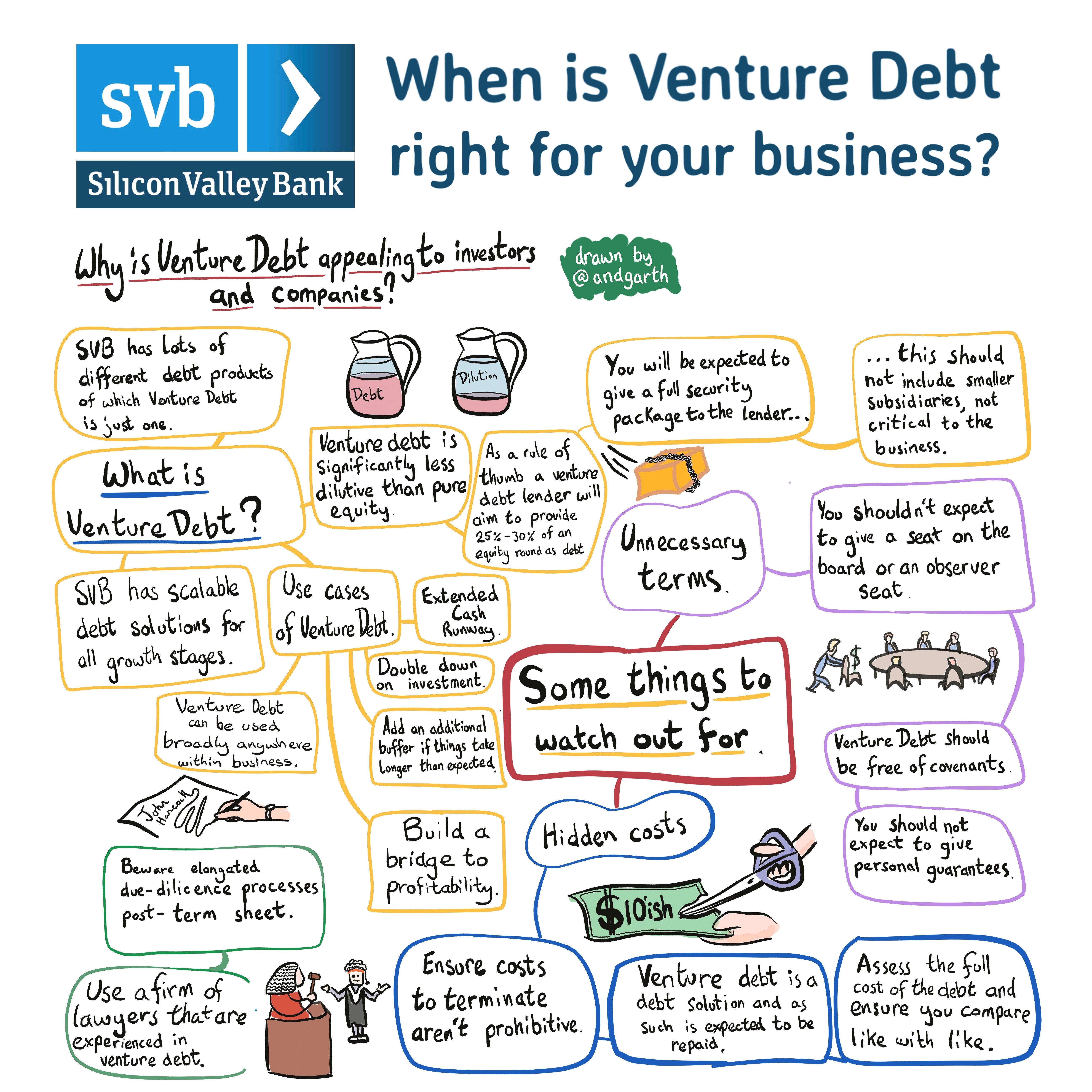
When Does Venture Debt Become Due?
Venture debt is a popular financing option for startups that have a promising business model but require additional capital to grow. Unlike traditional debt, venture debt is typically provided by non-bank lenders who are willing to take on more risk in exchange for higher returns. However, as with any debt, there comes a time when it must be repaid. In this article, we will explore when venture debt becomes due and what startups need to know to stay on top of their repayment obligations.
Understanding Venture Debt Terms and Structures
Before we dive into when venture debt becomes due, it’s important to understand the terms and structures of this type of financing. Venture debt is typically structured as a loan with interest rates ranging from 8% to 12%. In addition to interest, lenders may also require warrants, which give them the right to purchase equity in the startup at a future date.
Venture debt loans typically have a term of 24 to 36 months and are often structured with a “bullet” payment at the end of the term. This means that the entire principal and any outstanding interest are due at once, rather than being paid back in installments.
When Does Venture Debt Become Due?
The exact timing of when venture debt becomes due will depend on the terms of the loan agreement. However, there are several common triggers that can accelerate repayment obligations.
One such trigger is a change of control event, which occurs when a startup is acquired by another company. In this case, the entire principal and any outstanding interest on the venture debt loan become due immediately.
Another trigger is a default on the loan, which can occur if a startup fails to meet its repayment obligations or breaches other terms of the loan agreement. In this case, the lender may accelerate the repayment schedule and demand immediate payment of the outstanding balance.
Managing Venture Debt Repayment Obligations
To avoid defaulting on venture debt and facing the consequences of accelerated repayment, startups should have a plan in place to manage their repayment obligations. This plan should include a clear understanding of the loan terms and repayment schedule, as well as a strategy for generating sufficient cash flow to meet these obligations.
One way to manage venture debt repayment obligations is to negotiate for more flexible repayment terms upfront. For example, startups can negotiate for a longer repayment term or an installment payment schedule rather than a bullet payment.
Another strategy is to plan for potential exits or funding rounds that can provide the necessary cash flow to repay the debt. Startups can also explore refinancing options or seek out additional funding sources to pay off the debt.
The Benefits of Venture Debt
Despite the potential risks and repayment obligations, venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups. Some of the benefits of venture debt include:
- Lower dilution compared to equity financing
- Access to additional capital to fund growth
- Opportunities to build relationships with non-bank lenders
- The ability to leverage debt to increase returns for equity investors
Venture Debt vs. Other Financing Options
Venture debt is just one of many financing options available to startups. Other options include equity financing, traditional bank loans, and crowdfunding. Each financing option has its own pros and cons, and startups should carefully consider their options before making a decision.
Compared to equity financing, venture debt can be a more attractive option for startups that want to avoid dilution of their ownership stake. However, it also comes with the added risk of repayment obligations and potential default.
Compared to traditional bank loans, venture debt lenders are often more willing to take on risk and provide financing to startups with limited assets or revenue. However, interest rates and other terms may be less favorable than traditional bank loans.
Conclusion
Venture debt can be an effective way for startups to access additional capital to fund growth without diluting their ownership stake. However, it’s important for startups to understand the terms and repayment obligations of this financing option to avoid default and other negative consequences. By negotiating for flexible repayment terms and having a sound plan in place to manage repayment obligations, startups can take advantage of the benefits of venture debt while minimizing its risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about venture debt:
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of financing that is typically provided to startups and other high-growth companies. Unlike equity financing, which involves selling ownership in the company, venture debt involves borrowing money that must be paid back with interest.
Venture debt can be a useful way for companies to raise capital without diluting ownership or giving up control. It is often used to fund growth initiatives, such as hiring new employees, expanding into new markets, or developing new products or services.
How does venture debt work?
Venture debt typically involves a loan agreement between the borrower (the company) and the lender (a bank or other financial institution). The loan agreement will specify the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, repayment period, and any other fees or charges.
Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is often structured with warrants or other equity-like features that give the lender the potential to share in the company’s future success. This can include the right to purchase stock in the company at a discounted price, or to receive a percentage of the company’s future revenue or profits.
What are the advantages of venture debt?
Venture debt can offer several advantages for companies seeking to raise capital. For one, it can provide a source of funding without diluting ownership or giving up control. This can be especially important for startups and other high-growth companies that want to retain as much ownership as possible.
Venture debt can also be faster and easier to obtain than equity financing, which can involve lengthy negotiations and due diligence processes. Additionally, venture debt can be less expensive than other types of debt financing, such as convertible debt or mezzanine financing.
When does venture debt become due?
Venture debt typically comes with a repayment period that can range from a few months to several years. The repayment period will be specified in the loan agreement, along with the interest rate and any other terms of the loan.
It is important for companies to understand when their venture debt is due so that they can plan accordingly and avoid defaulting on the loan. If a company is unable to repay its venture debt on time, it may face penalties or other consequences, such as a damaged credit rating or legal action from the lender.
What happens if a company can’t repay its venture debt?
If a company is unable to repay its venture debt on time, it may face penalties or other consequences as specified in the loan agreement. This can include additional fees or charges, increased interest rates, or legal action from the lender.
In some cases, the lender may also have the right to take ownership or control of the company’s assets or operations in order to recover the debt. It is important for companies to carefully review the terms of their venture debt agreements and plan accordingly to avoid defaulting on the loan.
The Value of Venture Debt Explained – Trinity Capital Inc.
In conclusion, the timing of when venture debt becomes due is a crucial consideration for entrepreneurs and investors alike. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, companies typically have between two and four years to repay the loan.
It is important to keep in mind that venture debt can be a powerful tool for growth, but it comes with risks. Entrepreneurs should carefully consider their cash flow projections and ensure they have a plan in place to repay the loan on time.
Ultimately, venture debt can provide a valuable source of capital for startups looking to scale quickly. As long as companies do their due diligence and plan accordingly, they can benefit from the advantages of venture debt while mitigating the risks.
