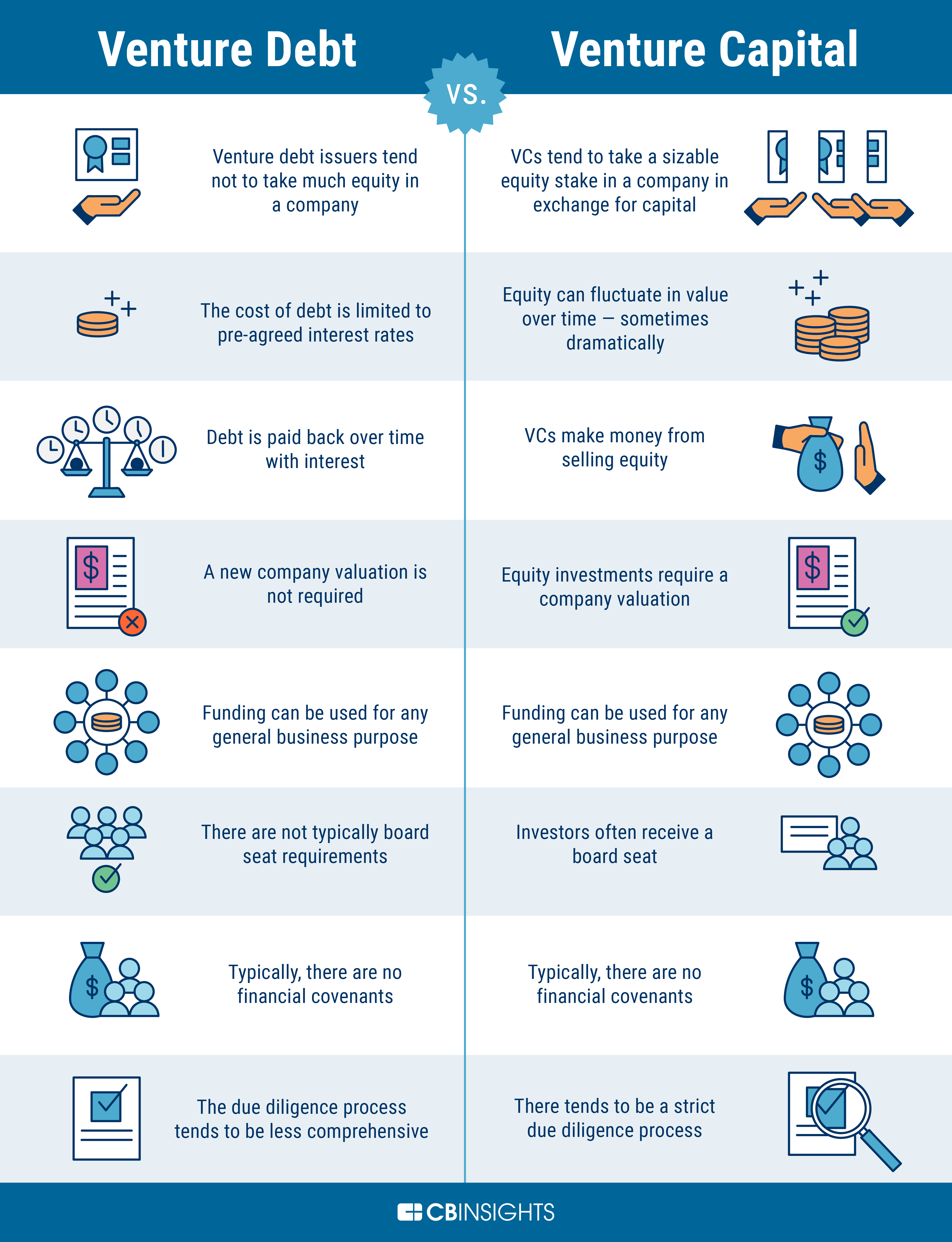
Venture debt is a type of financing that has become increasingly popular among startups and emerging businesses. It is a form of debt financing that enables companies to obtain capital without diluting equity.
Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of startups. It is often used to supplement equity financing and can be a valuable tool for companies looking to scale quickly while preserving ownership and control. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of venture debt and how it can benefit your business.
What is Venture Debt?
Venture Debt is a type of financing that allows startups and early-stage companies to borrow money to finance their growth. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is designed specifically for startups and is often provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs and challenges of these companies.
How Does Venture Debt Work?
Venture debt works by providing startups with a loan that is secured by the company’s assets, such as intellectual property or equipment. This type of financing is often used to supplement equity financing, which is typically provided by venture capitalists or angel investors. Venture debt can be used to fund a variety of activities, including product development, marketing, and working capital.
Venture debt lenders typically require the borrower to meet certain financial metrics, such as revenue growth or profitability, to ensure that the company is on track to achieve its goals. The loan is usually structured with a fixed interest rate and a set repayment schedule, which can range from a few months to several years.
Benefits of Venture Debt
There are several benefits to using venture debt financing for startups and early-stage companies. One of the main advantages is that it allows companies to raise capital without diluting their ownership or giving up control of the company. This is because venture debt lenders do not typically require an equity stake in the company as a condition of the loan.
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can help companies maintain a steady cash flow, which is important for startups that may not have steady revenue streams. The fixed interest rate and repayment schedule also provide predictability and stability for the company’s finances.
Types of Venture Debt
There are several types of venture debt that startups can use to finance their growth. The most common types include:
- Equipment Financing – This type of venture debt is used to purchase equipment or other assets that can be used as collateral for the loan.
- Convertible Debt – This type of venture debt can be converted into equity at a later date, providing the lender with the potential for a higher return on their investment.
- Accounts Receivable Financing – This type of venture debt is based on the company’s accounts receivable, which are used as collateral for the loan.
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
Venture debt and equity financing are two different ways for startups to raise capital, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. One of the main differences between the two is that equity financing involves selling a portion of the company to investors in exchange for funding, while venture debt involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest.
Equity financing can be a good option for startups that are looking to raise a significant amount of capital and are willing to give up some ownership of the company. Venture debt, on the other hand, can be a good option for startups that want to maintain control of their company and avoid dilution of ownership.
Risks of Venture Debt
While venture debt can be a useful tool for startups, it also comes with some risks. One of the main risks is that the company may not be able to repay the loan, which can lead to default and potentially bankruptcy. Another risk is that the lender may require the company to provide additional collateral or other guarantees, which can put additional strain on the company’s finances.
Choosing a Venture Debt Lender
When choosing a venture debt lender, it’s important to look for a lender that has experience working with startups and understands the unique needs and challenges of these companies. It’s also important to carefully review the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, repayment schedule, and any collateral requirements.
Conclusion
Venture debt can be a useful tool for startups and early-stage companies that are looking to finance their growth without giving up equity or control of their company. By understanding the benefits and risks of venture debt, as well as the different types of financing available, startups can make informed decisions about their financing options and choose the option that best meets their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the characteristics of venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of financing that is typically used by startups and high-growth companies that have limited access to traditional bank loans. Unlike equity financing, venture debt involves borrowing money from a lender, typically with a fixed interest rate and a set repayment schedule. Venture debt is often used to bridge funding gaps between equity rounds or to finance specific growth initiatives. It is also typically secured by the company’s assets, such as its intellectual property, equipment, or accounts receivable.
Venture debt is generally considered less risky than equity financing because the lender has a claim on the company’s assets in the event of default. However, it typically comes with higher interest rates and fees than traditional bank loans, and may also include warrants or other equity-like features.
What are the advantages of using venture debt?
There are several advantages to using venture debt as a source of financing. First, it can help companies extend their cash runway and achieve key milestones without diluting existing shareholders. Second, it can be a more flexible and cost-effective alternative to equity financing, particularly for companies that are not yet profitable or have limited collateral. Third, venture debt lenders may also provide valuable strategic advice and introductions to potential investors or acquirers.
However, it’s important to note that venture debt is not suitable for all types of companies or situations. Companies that are already highly leveraged or have limited revenue visibility may struggle to secure favorable terms, and may also face higher risks of default.
How does venture debt differ from traditional bank loans?
Venture debt differs from traditional bank loans in several key ways. First, venture debt lenders tend to be more focused on the company’s growth prospects and potential for future equity financing, rather than its current financial performance. As a result, they may be more willing to lend to companies that have limited revenue or cash flow.
Second, venture debt is typically secured by the company’s assets, rather than its cash flow or creditworthiness. This means that lenders may be more willing to extend credit to companies that have limited collateral, such as early-stage startups.
Finally, venture debt typically comes with higher interest rates, fees, and other covenants than traditional bank loans. Lenders may also require warrants or other equity-like features as part of the financing package.
What are the risks of using venture debt?
As with any type of financing, there are risks associated with using venture debt. One of the biggest risks is default, which can result in the lender seizing the company’s assets and potentially forcing it into bankruptcy. Other risks include higher interest rates, fees, and covenants than traditional bank loans, as well as potential dilution of existing shareholders if the lender requires warrants or other equity-like features.
It’s important for companies to carefully evaluate their cash flow projections and ability to meet the repayment schedule before taking on venture debt. Companies should also be aware of the lender’s reputation and track record, as well as any potential conflicts of interest that may arise.
How do I know if venture debt is right for my company?
Deciding whether or not to use venture debt as a source of financing depends on a number of factors, including the company’s growth prospects, cash flow projections, and existing capital structure. Companies that are looking to extend their cash runway or finance specific growth initiatives may find venture debt to be a flexible and cost-effective alternative to equity financing.
However, it’s important to carefully evaluate the terms of any venture debt financing, including interest rates, fees, and covenants, as well as the lender’s reputation and track record. Companies should also consider the potential risks and downsides of venture debt, including the potential for default and dilution of existing shareholders. Ultimately, the decision to use venture debt should be based on a careful analysis of the company’s financing needs and goals.
What is Venture Debt and why invest in it?
In conclusion, venture debt is a financing option that can provide startups with additional capital to fuel growth and expansion. It is a form of debt financing that is typically offered by specialized lenders, and it comes with certain advantages and disadvantages.
On the one hand, venture debt can allow startups to raise capital without diluting their ownership stake or giving up control of their company. Additionally, venture debt can be structured in a way that is more flexible than traditional debt financing, allowing startups to manage their cash flow more effectively.
On the other hand, venture debt can be more expensive than other forms of financing, and it typically comes with more restrictions and covenants. Startups that are considering venture debt should carefully weigh the costs and benefits of this financing option before making a decision.
Overall, venture debt can be a valuable tool for startups that are looking to raise capital and grow their business. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of this financing option, startups can make informed decisions about their financing strategy and position themselves for long-term success.
