Venture debt and venture capital are two popular options for startups looking for funding. While venture capital has long been the preferred choice for many entrepreneurs, venture debt has emerged as a viable alternative. In this article, we will explore the advantages of venture debt over venture capital, and how it can help startups grow their businesses without diluting equity or giving up control.
If you’re a startup founder seeking funding, you may be wondering which option is best for your business. While both venture debt and venture capital have their pros and cons, venture debt offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for many startups. From lower equity dilution to more flexible repayment terms, venture debt can provide the financial support you need to take your business to the next level.
Advantages of Venture Debt over Venture Capital
Venture debt and venture capital are two popular financing options available for startups and growing businesses. While both have their own advantages and disadvantages, venture debt has emerged as a preferred option for many companies. In this article, we will discuss the advantages of venture debt over venture capital.
1. Lower Dilution
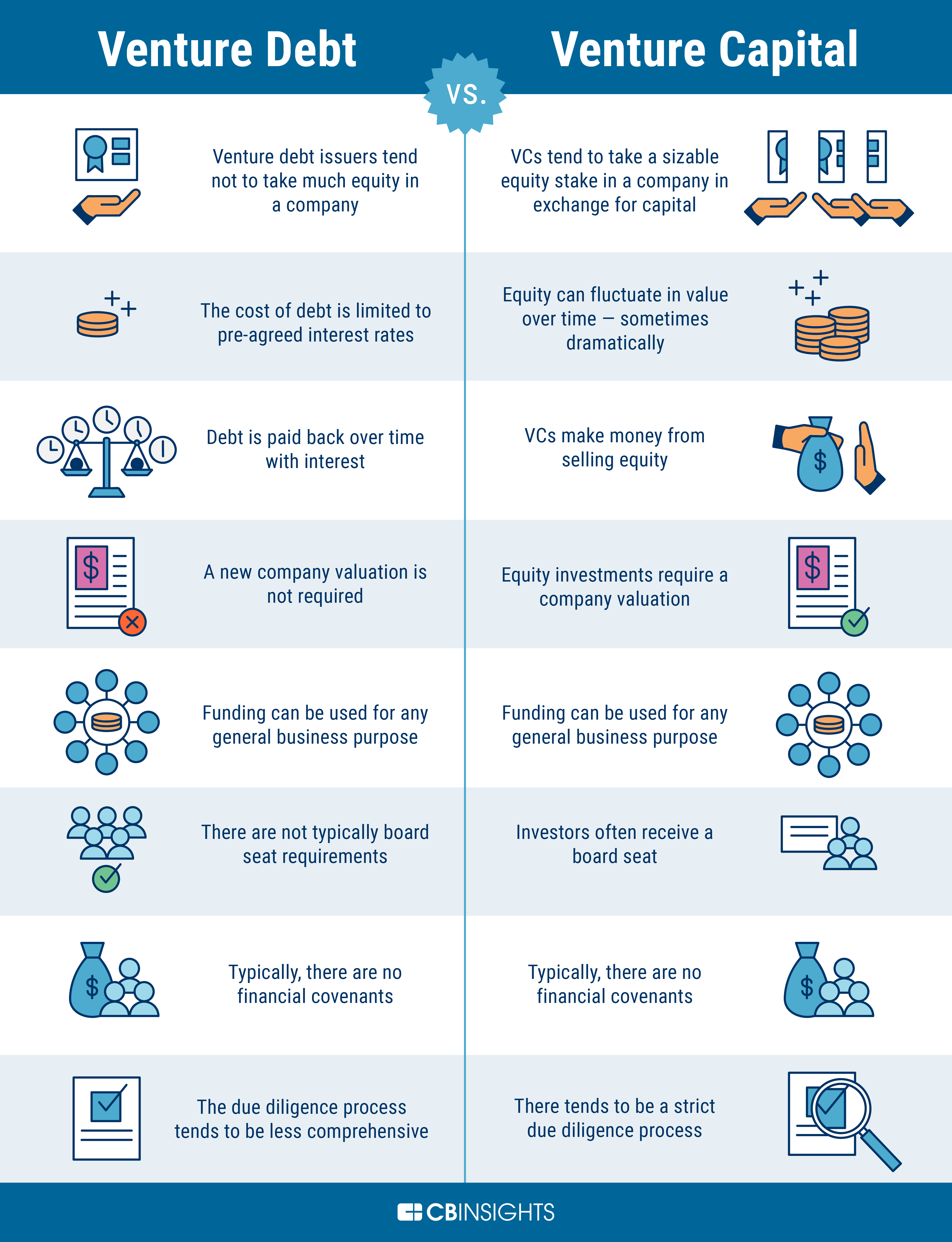
Venture debt involves borrowing money from a lender, which is usually a bank or a specialty finance company. Unlike venture capital, there is no equity involved, and the company does not have to give up any ownership stake. This means that the company’s existing shareholders do not get diluted, and they retain control over the company’s decision-making process.
Moreover, venture debt is typically structured as a loan with a fixed interest rate and a maturity date. This means that the company knows exactly how much it has to pay back and when, which helps with budgeting and forecasting.
2. Increased Valuation
When a company takes on venture capital, it usually involves selling a portion of the company’s equity to the investors. This means that the company’s valuation is determined by the investors, and it may not necessarily reflect the true value of the company.
On the other hand, venture debt does not affect the company’s valuation. This means that the company can continue to raise funds at a higher valuation, which can be beneficial when it comes to future fundraising rounds or potential acquisitions.
3. Faster Access to Capital
Raising venture capital can be a time-consuming process that involves pitching to multiple investors, negotiating terms, and going through due diligence. This process can take several months, if not longer.
In contrast, venture debt can be obtained relatively quickly, often within a few weeks. This can be especially helpful for companies that need capital to take advantage of a time-sensitive opportunity or to fund a specific project.
4. No Board Seats or Voting Rights
When a company takes on venture capital, the investors usually get a seat on the company’s board of directors and voting rights. This means that the investors have a say in the company’s decision-making process, which can sometimes lead to conflicts with the founders and other shareholders.
Venture debt, on the other hand, does not come with any board seats or voting rights. This means that the company’s existing shareholders can retain full control over the company’s operations and strategic direction.
5. Flexible Repayment Terms
Venture debt can be structured in a variety of ways, depending on the needs of the company. For example, it can be structured as a term loan with monthly payments, a line of credit with interest-only payments, or a convertible note that can be converted into equity in the future.
This flexibility allows companies to choose a repayment structure that works best for them, based on their cash flow and growth projections.
6. Lower Cost of Capital
While venture debt typically has a higher interest rate than traditional bank loans, it is usually cheaper than equity financing. This is because the lender is taking on less risk than an equity investor, and therefore does not require as high a return on investment.
Moreover, venture debt often comes with fewer fees and expenses than equity financing, which can also help to reduce the cost of capital for the company.
7. No Equity Dilution for Founders
When a company takes on venture capital, the founders usually have to give up a portion of their equity stake. This means that they may not fully benefit from the company’s success in the future.
With venture debt, the founders can retain their equity stake and fully benefit from the company’s growth and profitability. This can be especially important for companies that have a strong vision and want to maintain control over their business.
8. Better Alignment of Interests
When a company takes on venture capital, the investors are looking for a high return on investment, often within a relatively short timeframe. This can sometimes lead to conflicts with the founders and other shareholders, who may have a longer-term vision for the company.
Venture debt, on the other hand, is typically structured with a longer maturity date and a fixed interest rate. This means that the lender’s interests are more aligned with the company’s interests, and there is less pressure to achieve short-term results.
9. Access to Additional Funding
When a company takes on venture debt, it often establishes a relationship with a lender that can provide additional funding in the future. This can be especially helpful for companies that are looking to grow and expand their operations, as they can tap into this source of funding without having to go through the fundraising process again.
10. Lower Risk of Losing Control
When a company takes on venture capital, there is always a risk of losing control over the company’s decision-making process. This can happen if the investors disagree with the founders on key strategic decisions, or if the company fails to meet certain performance targets.
With venture debt, the company retains full control over its operations and strategic direction. As long as it meets its repayment obligations, there is no risk of losing control to a third-party investor.
In conclusion, venture debt offers a number of advantages over venture capital, including lower dilution, increased valuation, faster access to capital, and greater control over the company’s decision-making process. While it may not be the right financing option for every company, it is definitely worth considering for those that are looking to raise capital without giving up equity or control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is designed for startups and early-stage businesses. It provides a way for these companies to raise capital without giving up equity in their business. Venture debt is typically provided by banks, specialty lenders, or venture debt funds.
Venture debt is often used in conjunction with equity financing. By combining the two, startups can raise the capital they need to grow their business while minimizing dilution for their existing shareholders.
How is venture debt different from venture capital?
Venture debt is a form of debt financing, while venture capital is a form of equity financing. With venture debt, the lender provides the startup with a loan, which must be repaid with interest. With venture capital, the investor provides the startup with funding in exchange for equity in the company.
Because venture debt does not require the startup to give up equity, it can be a more attractive form of financing for founders who want to maintain control of their company. Additionally, venture debt can be easier and quicker to obtain than venture capital.
What are the advantages of venture debt over venture capital?
One of the primary advantages of venture debt is that it allows startups to raise capital without giving up equity. This can be particularly attractive to founders who want to maintain control of their company. Additionally, venture debt can be easier and quicker to obtain than venture capital.
Another advantage of venture debt is that it can be less dilutive than equity financing. Because the startup is borrowing money rather than selling shares, the lender does not become a shareholder in the company. As a result, the existing shareholders’ ownership percentages are not reduced.
What are the risks of venture debt?
One of the main risks of venture debt is that it can be more expensive than other forms of financing. Because the lender is taking on more risk by providing debt financing to startups, they may charge higher interest rates and fees than other lenders.
Another risk of venture debt is that it can be more difficult to obtain than other forms of financing. Because startups are typically higher-risk borrowers, lenders may require more stringent underwriting standards and collateral requirements. Additionally, venture debt may not be available to startups that do not have a strong track record or a solid business plan.
When is venture debt a good option for startups?
Venture debt can be a good option for startups that have a solid business plan and a strong track record of revenue growth. It can be particularly attractive to founders who want to maintain control of their company and minimize dilution for existing shareholders.
Additionally, venture debt can be a good option for startups that have already raised equity financing and are looking for additional capital to fund their growth. By combining equity and debt financing, startups can raise the capital they need to grow their business while minimizing dilution for their existing shareholders.
The Value of Venture Debt Explained – Trinity Capital Inc.
In conclusion, venture debt is becoming an increasingly attractive option for startups looking to secure funding. While venture capital may offer larger sums of money, the debt structure of venture debt provides startups with greater flexibility and control over their finances. Additionally, the interest rates and repayment terms are often more favorable than those of traditional bank loans.
Another advantage of venture debt is that it allows startups to retain more ownership and control over their company. With venture capital, investors typically take a percentage of equity in exchange for their investment, which can dilute the founders’ ownership and decision-making power. With venture debt, however, startups can secure the funding they need without sacrificing ownership or control.
Overall, while venture capital may be the better choice for some startups, venture debt offers several advantages that should not be overlooked. It provides greater flexibility, more favorable terms, and allows startups to retain more ownership and control over their company. As the startup landscape continues to evolve, venture debt is sure to become an increasingly popular option for founders looking to grow their business.
