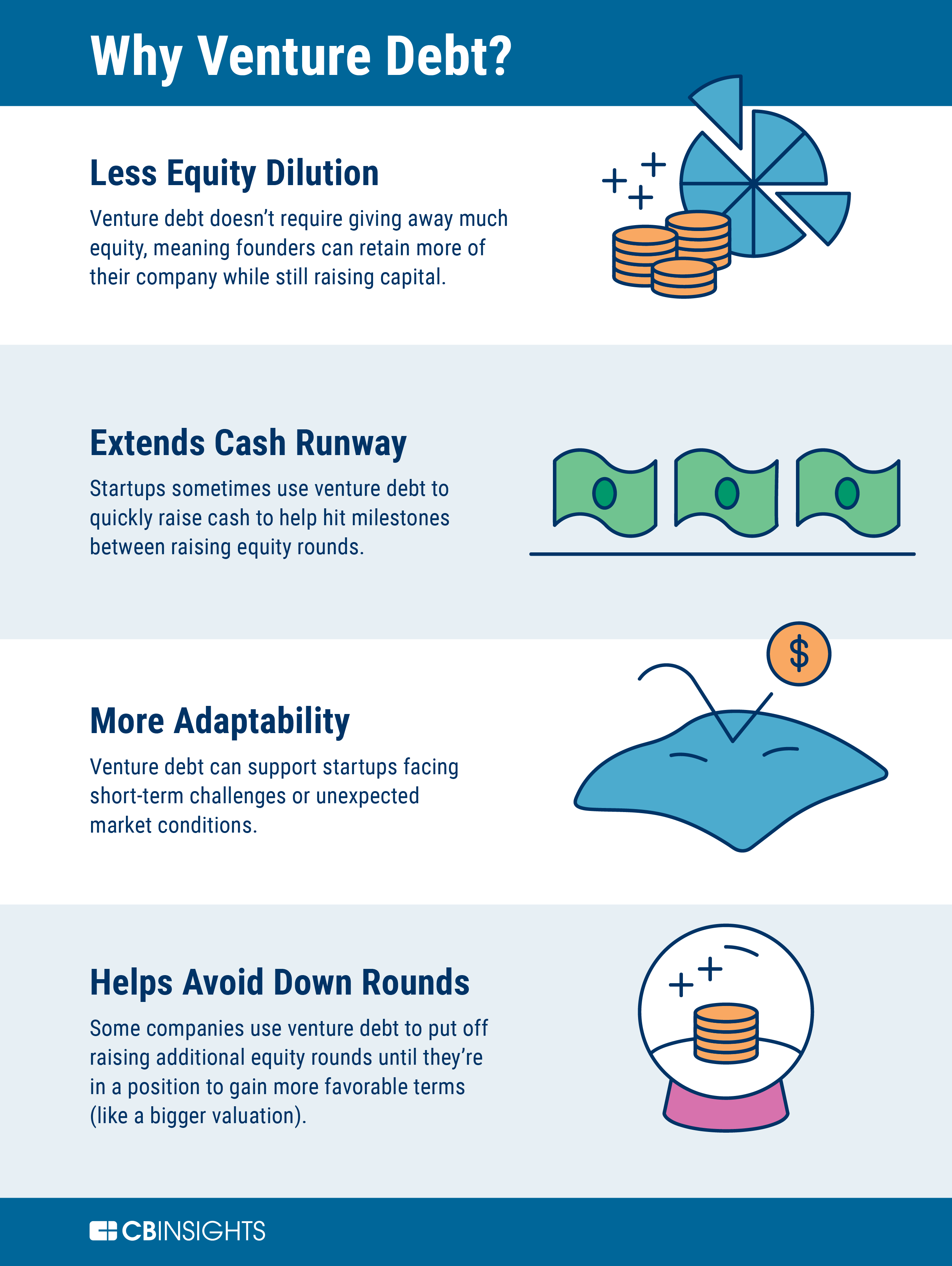
Venture debt can be a great way for startups to raise capital without diluting their equity. However, it’s not always a perfect solution. In some cases, venture debt has been known to contribute to the downfall of a company.
While venture debt can provide the much-needed financial boost for a startup, it also comes with risks. Some companies may take on too much debt, leaving them unable to make payments or hurting their credit score. If not managed properly, venture debt can lead to a company’s failure. In this article, we’ll explore some of the cases where venture debt has had a negative impact on startups and what can be done to prevent it.
The Risks of Venture Debt: Can it Lead to Company Failure?
What is Venture Debt?
Venture debt is a form of financing that provides companies with debt capital in addition to equity financing. This type of funding is often used by early-stage startups and high-growth companies to supplement their equity financing, usually in the form of venture capital. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically unsecured, meaning that it is not backed by collateral.
Venture debt can be an attractive financing option for companies that want to maintain control and ownership of their business while still raising capital. However, this form of financing also comes with certain risks that companies should be aware of.
The Risks of Venture Debt
While venture debt can be an effective way to raise capital, it also comes with certain risks that companies should be aware of. Some of the most significant risks associated with venture debt include:
1. High-Interest Rates: Venture debt typically comes with higher interest rates than traditional bank loans, which can make it more expensive for companies to borrow money.
2. Restrictive Terms: Venture debt agreements often come with restrictive terms that can limit a company’s flexibility and make it more difficult to operate. For example, some venture debt agreements may require a company to maintain certain financial ratios or limit its ability to raise additional capital.
3. Limited Capital: Venture debt typically provides companies with a smaller amount of capital than equity financing, which can make it harder for companies to achieve their growth objectives.
4. Lack of Control: Unlike equity financing, venture debt does not provide investors with ownership or control over a company. However, venture debt agreements may include covenants that give lenders certain control rights over a company, such as the ability to appoint a board member or veto certain strategic decisions.
Examples of Venture Debt Failures
While venture debt can be an effective financing option for companies, there have been cases where it has led to company failures. One example is the case of MyDoom, a Silicon Valley startup that raised $95 million in funding, including $25 million in venture debt. Despite this significant amount of funding, the company ultimately failed due to a combination of factors, including poor management and a lack of product-market fit.
Another example is the case of Zirtual, a virtual assistant startup that raised $5.5 million in funding, including $3.4 million in venture debt. The company ultimately failed due to a cash crunch caused by poor financial management and a lack of profitability.
Benefits of Venture Debt
Despite the risks associated with venture debt, there are also several benefits that companies should consider. Some of the most significant benefits of venture debt include:
1. Lower Dilution: Unlike equity financing, venture debt does not require companies to give up ownership or control over their business. This can be particularly attractive for companies that want to maintain control over their operations and avoid dilution of their equity.
2. Faster Financing: Venture debt can be a faster and more efficient way to raise capital than equity financing. This is because venture debt agreements are typically less complex and require less due diligence than equity financing agreements.
3. Supplemental Capital: Venture debt can be an effective way to supplement equity financing and provide companies with additional capital to fuel their growth objectives.
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
When considering venture debt as a financing option, it’s important for companies to understand how it compares to equity financing. Some of the key differences between venture debt and equity financing include:
1. Ownership and Control: Equity financing typically involves giving up ownership and control over a company in exchange for funding, while venture debt does not.
2. Cost of Capital: Venture debt typically comes with a higher cost of capital than equity financing, due to the higher interest rates associated with debt financing.
3. Amount of Capital: Equity financing typically provides companies with a larger amount of capital than venture debt, which can make it easier for companies to achieve their growth objectives.
4. Risk: Equity financing is typically considered a higher-risk financing option than venture debt, due to the potential for dilution of ownership and control over a company.
Conclusion
Venture debt can be an attractive financing option for companies that want to supplement their equity financing and maintain control over their business. However, it also comes with certain risks that companies should be aware of, including high-interest rates, restrictive terms, limited capital, and lack of control. By carefully considering the benefits and risks associated with venture debt, companies can make an informed decision about whether this type of financing is right for them.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about venture debt and its impact on companies:
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of financing that involves borrowing money from a lender with the expectation of paying it back over time with interest. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt typically involves equity-like features such as warrants or convertible debt.
It can be an attractive option for startups that need additional capital but don’t want to dilute ownership or give up control of their company. However, it can also be risky, as the interest rates are often higher than traditional loans, and the debt can become a burden if the company is not able to generate enough revenue to pay it back.
What are some examples of companies that have used venture debt successfully?
There are many examples of companies that have used venture debt to their advantage and gone on to achieve great success. One notable example is the online retailer Zulily, which used venture debt to fund its growth and eventually went public with a valuation of over $2 billion.
Another example is the software company Hubspot, which used venture debt to finance its expansion and later went public with a valuation of over $1 billion. These companies were able to use venture debt strategically to fuel their growth without sacrificing equity or control.
What are some risks associated with venture debt?
While venture debt can be a useful tool for startups, it is not without its risks. One of the biggest risks is the high interest rates associated with this type of financing, which can quickly become a burden if the company is not able to generate enough revenue to pay it back.
Another risk is the potential for the lender to exercise their equity-like features, such as warrants or convertible debt, which can lead to dilution of ownership or control. Additionally, if the company is not able to achieve its growth targets, it may struggle to secure additional financing in the future.
How can companies mitigate the risks associated with venture debt?
There are several strategies that companies can use to mitigate the risks associated with venture debt. One is to carefully evaluate the terms of the loan and ensure that they are not taking on more debt than they can realistically handle.
Another strategy is to have a clear plan for how the borrowed funds will be used and how the company plans to generate revenue to pay back the loan. Additionally, companies can work to build strong relationships with their lenders and maintain open lines of communication to address any issues that may arise.
What are some examples of companies that have failed as a result of venture debt?
While venture debt can be a useful financing tool, there are also examples of companies that have failed as a result of taking on too much debt. One notable example is the online retailer Fab.com, which raised over $300 million in venture debt and equity before ultimately failing to achieve profitability and shutting down in 2015.
Another example is the mobile analytics company Flurry, which raised over $60 million in venture debt and equity before being acquired by Yahoo for a fraction of its previous valuation. These examples highlight the importance of carefully evaluating the risks and benefits of venture debt before deciding to pursue this type of financing.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, while venture debt can be a useful tool for startups looking to raise capital, it is not without its risks. There have been cases where companies have failed as a result of taking on too much debt, or not being able to meet the repayment terms. However, it is important to remember that these cases are the exception rather than the rule.
It is also worth noting that venture debt can be a valuable option for companies that are confident in their ability to grow and generate revenue, and that have a clear plan for how they will use the funds they raise. By taking a strategic approach to debt financing, startups can use venture debt to accelerate their growth and achieve their goals more quickly.
Ultimately, the decision to take on venture debt will depend on a variety of factors, including the company’s financial situation, growth prospects, and risk tolerance. As with any form of financing, it is important for startups to carefully evaluate the potential risks and benefits before making a decision, and to work closely with experienced advisors who can help them navigate the process.
