Venture debt is a popular method of financing for startups and growing businesses. It allows companies to raise funds without giving up equity, and is often used in conjunction with equity financing. However, the way venture debt works can vary greatly from country to country, and understanding these differences is critical for companies seeking to expand globally.
In this article, we’ll explore the nuances of venture debt in different countries, including the types of lenders, the terms and conditions of the loans, and the legal and regulatory frameworks that govern them. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how venture debt works around the world, and be better equipped to navigate this complex and important aspect of global business.
How Does Venture Debt Work in Different Countries?
Venture debt is a financing option used by startup companies to raise capital for growth and expansion. It is a form of debt financing that is secured by the company’s assets, and it is typically used in conjunction with equity financing. While venture debt is a popular option for startups in the United States, it is also gaining popularity in other countries. In this article, we will explore how venture debt works in different countries.
1. Venture Debt in the United States
Venture debt has been a popular financing option for startups in the United States for many years. In the US, venture debt is typically provided by banks, venture debt funds, and other financial institutions. The terms of venture debt in the US can vary depending on the lender, but typically, the interest rates are higher than traditional bank loans. However, venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups because it allows them to raise capital without diluting their equity.
One of the benefits of venture debt in the US is that it is often structured as a line of credit, which means that the company can draw down on the funds as needed. This can be particularly helpful for startups that have unpredictable cash flows. Additionally, venture debt in the US is often structured with warrants, which gives the lender the right, but not the obligation, to purchase equity in the company at a future date.
2. Venture Debt in Europe
Venture debt is also gaining popularity in Europe as a financing option for startups. In Europe, venture debt is typically provided by banks, venture debt funds, and other financial institutions. The terms of venture debt in Europe are similar to those in the US, with higher interest rates than traditional bank loans.
One of the benefits of venture debt in Europe is that it is often structured as a mezzanine financing option, which means that it sits between debt and equity financing. This can be particularly helpful for startups that are not yet ready for equity financing but need more capital than traditional bank loans can provide.
3. Venture Debt in Asia
Venture debt is also gaining popularity in Asia as a financing option for startups. In Asia, venture debt is typically provided by banks, venture debt funds, and other financial institutions. The terms of venture debt in Asia are similar to those in the US and Europe, with higher interest rates than traditional bank loans.
One of the unique features of venture debt in Asia is that it is often provided by local banks, which can be advantageous for startups that are operating in the region. Additionally, venture debt in Asia is often structured with a lower interest rate than in other regions, which can be helpful for startups that are looking to conserve cash.
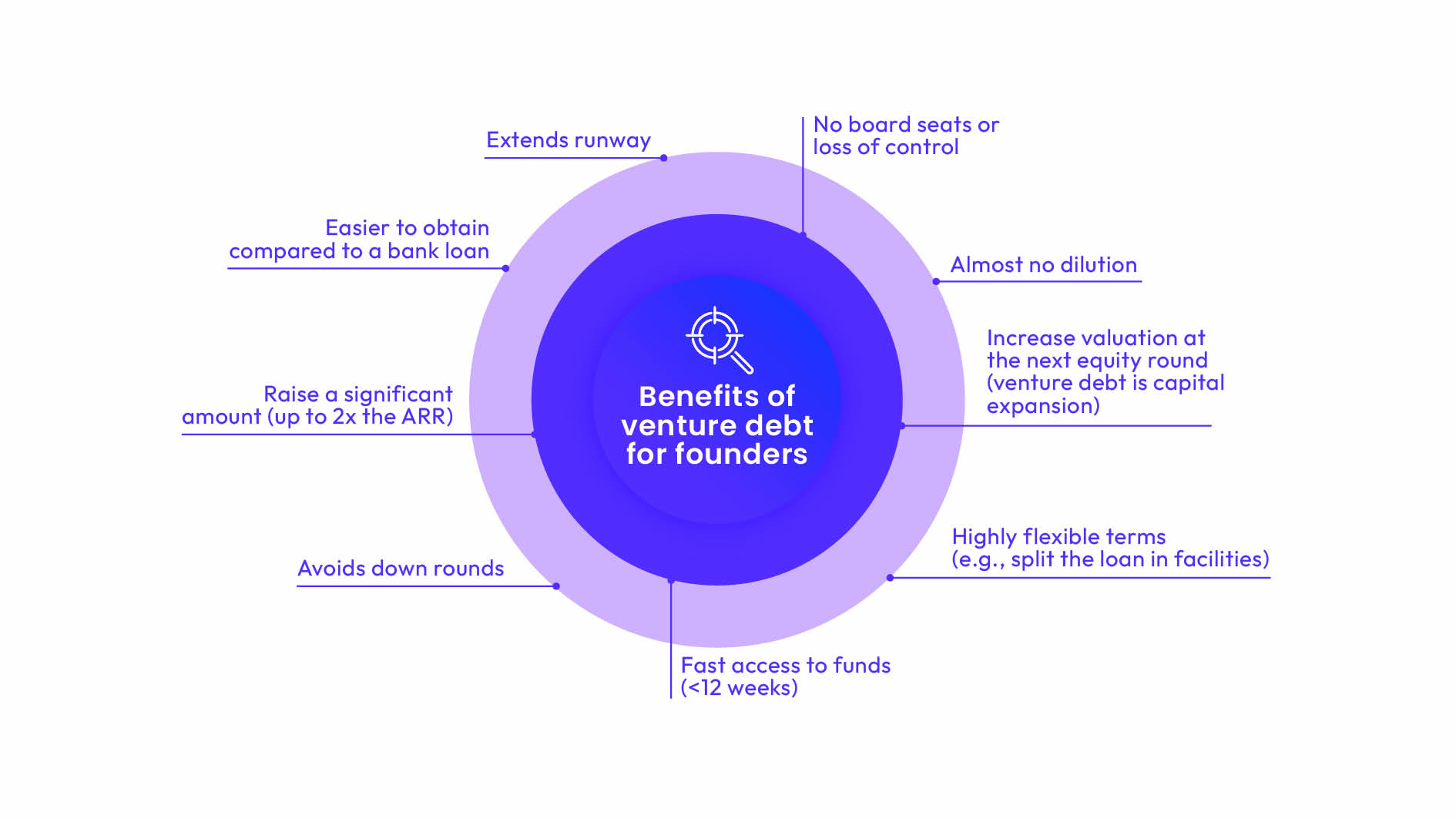
4. Benefits of Venture Debt
Venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups for several reasons. First, it allows startups to raise capital without diluting their equity. This can be particularly helpful for startups that are not yet ready for equity financing or that want to preserve their equity for future rounds of financing.
Second, venture debt is often structured as a line of credit, which means that the company can draw down on the funds as needed. This can be particularly helpful for startups that have unpredictable cash flows or that need to finance specific projects or initiatives.
Third, venture debt is often structured with warrants, which gives the lender the right, but not the obligation, to purchase equity in the company at a future date. This can be beneficial for startups because it allows them to raise capital at a lower cost than they would with equity financing.
5. Risks of Venture Debt
While venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups, it also comes with risks. One of the primary risks of venture debt is that it is secured by the company’s assets. This means that if the company is unable to repay the debt, the lender can seize the company’s assets to recover their investment.
Another risk of venture debt is that the interest rates are typically higher than traditional bank loans. This can make venture debt a more expensive form of financing for startups.
6. Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
Venture debt and equity financing are two of the primary financing options for startups. While both options can be valuable, they have different advantages and disadvantages.
One of the primary advantages of equity financing is that it allows startups to raise large amounts of capital without taking on debt. Additionally, equity financing can provide startups with access to experienced investors who can provide valuable guidance and support.
On the other hand, venture debt allows startups to raise capital without diluting their equity. Additionally, venture debt is often structured as a line of credit, which means that the company can draw down on the funds as needed.
7. Venture Debt vs. Traditional Bank Loans
Venture debt and traditional bank loans are two financing options that are often compared. While both options can be valuable, they have different advantages and disadvantages.
One of the primary advantages of venture debt over traditional bank loans is that it allows startups to raise capital without diluting their equity. Additionally, venture debt is often structured as a line of credit, which means that the company can draw down on the funds as needed.
On the other hand, traditional bank loans typically have lower interest rates than venture debt. Additionally, traditional bank loans do not require the company to provide warrants, which means that the lender does not have the right to purchase equity in the company at a future date.
8. Venture Debt Fundamentals
When considering venture debt as a financing option, it is important to understand the fundamentals. Venture debt is a form of debt financing that is secured by the company’s assets. The terms of venture debt can vary depending on the lender, but typically, the interest rates are higher than traditional bank loans.
Additionally, venture debt is often structured as a line of credit, which means that the company can draw down on the funds as needed. Venture debt is often structured with warrants, which gives the lender the right, but not the obligation, to purchase equity in the company at a future date.
9. Venture Debt Strategies
There are several strategies that startups can use when considering venture debt as a financing option. One strategy is to use venture debt to bridge the gap between equity rounds. This can be particularly helpful for startups that are not yet ready for equity financing but need more capital than traditional bank loans can provide.
Another strategy is to use venture debt to finance specific projects or initiatives. For example, a startup may use venture debt to finance the development of a new product or to expand into a new market.
10. Conclusion
Venture debt is a valuable financing option for startups that are looking to raise capital for growth and expansion. While the terms of venture debt can vary depending on the lender and the region, it is a popular option in the United States, Europe, and Asia.
When considering venture debt as a financing option, it is important to understand the fundamentals and the risks. Additionally, startups should consider their specific financing needs and goals when deciding whether to use venture debt as a financing option.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is typically provided to early-stage, high-growth companies. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is usually provided by specialized lenders who are familiar with the needs and risks of startups. Venture debt can be an attractive form of financing for companies that are not yet profitable but have strong growth prospects.
Venture debt can take many forms, including term loans, lines of credit, and convertible notes. The terms of venture debt are generally more flexible than traditional bank loans, and often include warrants or other equity-like features that give the lender the opportunity to participate in the upside potential of the borrower.
How does venture debt work in the United States?
In the United States, venture debt is a well-established form of financing for early-stage companies. There are many specialized lenders who provide venture debt, and the terms of these loans can be quite favorable for borrowers. In general, venture debt in the US is structured as a term loan or a line of credit, and often includes warrants or other equity features.
Venture debt is often used by US companies to extend their cash runway and avoid dilution. By using venture debt to fund their growth, companies can delay raising additional equity capital, which can be expensive and dilutive.
How does venture debt work in Europe?
Venture debt is becoming more popular in Europe as a form of financing for early-stage companies. However, the market for venture debt in Europe is less developed than in the US, and there are fewer specialized lenders.
In Europe, venture debt is typically structured as a term loan or a convertible note, and often includes warrants or other equity features. The terms of venture debt in Europe are generally less favorable than in the US, reflecting the higher risk profile of early-stage companies in Europe.
How does venture debt work in Asia?
Venture debt is also becoming more popular in Asia as a form of financing for early-stage companies. However, the market for venture debt in Asia is even less developed than in Europe, and there are fewer specialized lenders.
In Asia, venture debt is typically structured as a term loan or a convertible note, and often includes warrants or other equity features. The terms of venture debt in Asia are generally less favorable than in the US or Europe, reflecting the higher risk profile of early-stage companies in Asia.
What are the risks and benefits of venture debt?
The main benefit of venture debt is that it can provide early-stage companies with additional capital to fund their growth, without diluting the ownership of the existing shareholders. Venture debt can also be less expensive than equity financing, since the interest rates on venture debt are generally lower than the cost of equity.
However, there are also risks associated with venture debt. Since venture debt is a form of debt, companies that take on venture debt are taking on additional financial risk. If the company is not able to generate sufficient cash flow to meet its debt obligations, it may be forced to default on its loans, which can be catastrophic for the company and its shareholders.
Additionally, since venture debt often includes equity features, companies that take on venture debt may be giving up some ownership or control over their company. This can be a significant drawback for companies that are looking to maintain full control over their operations.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, venture debt is a useful alternative financing option for startups looking to fuel their growth without diluting their ownership stakes. However, the nuances of venture debt can vary significantly depending on the country in question.
In countries like the United States, venture debt is a well-established and mature market, with a wide range of lenders and products available to startups. As a result, startups in the US have access to a more diverse range of debt options, including convertible notes, term loans, and lines of credit.
In contrast, in less mature markets like India and China, venture debt is still a relatively new concept, with fewer lenders and products available. However, as these countries continue to experience rapid economic growth, it is likely that venture debt will become an increasingly popular option for startups looking to raise capital. Overall, it is important for startups to understand the unique characteristics of venture debt in their respective countries before deciding whether or not it is the right financing option for their business.
