Venture debt can be an attractive financing option for startups looking to grow and expand. However, it’s important to understand how this type of debt can impact shareholder equity. In this article, we will explore the relationship between venture debt and shareholder equity, and dive into the potential benefits and drawbacks of this financing option. So, grab your coffee and let’s dive in!
Understanding the Impact of Venture Debt on Shareholder Equity
Venture debt is a popular financing option for startups and early-stage companies. It allows them to raise capital without diluting their ownership stake or giving up control of their company. However, it’s important to understand how venture debt can affect shareholder equity. In this article, we’ll examine the impact of venture debt on shareholder equity and how it can be used strategically to achieve business goals.
What is Venture Debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is provided to startups and early-stage companies. This type of financing is typically provided by banks, specialty lenders, or venture debt funds. Unlike traditional debt financing, venture debt is often structured as a loan with warrants or equity options attached.
One of the key benefits of venture debt is that it allows companies to raise capital without diluting their ownership stake or giving up control of their company. This is because venture debt is typically provided as a loan, which means that the lender has no ownership stake in the company. Instead, the lender receives interest payments and may also receive warrants or equity options that allow them to purchase shares of the company at a later date.
The Impact of Venture Debt on Shareholder Equity
While venture debt can provide a number of benefits to startups and early-stage companies, it’s important to understand how it can impact shareholder equity. One of the key ways that venture debt can impact shareholder equity is through the use of warrants or equity options.
When a company issues warrants or equity options to a venture debt lender, it effectively creates a new class of shares that can dilute the ownership stake of existing shareholders. This is because the lender may exercise their warrants or equity options at a later date, which can increase the total number of shares outstanding and reduce the percentage of ownership held by existing shareholders.
However, it’s important to note that the impact of venture debt on shareholder equity will depend on the specific terms of the financing agreement. For example, if the warrants or equity options are structured in a way that limits their impact on shareholder equity, then the impact may be minimal.
Strategic Uses of Venture Debt
Despite the potential impact on shareholder equity, venture debt can be used strategically to achieve important business goals. Some of the key strategic uses of venture debt include:
1. Increasing cash runway: Venture debt can help companies extend their cash runway, which can be critical for startups and early-stage companies that are still in the process of developing their products or services.
2. Accelerating growth: Venture debt can also be used to fund growth initiatives, such as expanding sales and marketing efforts or investing in new product development.
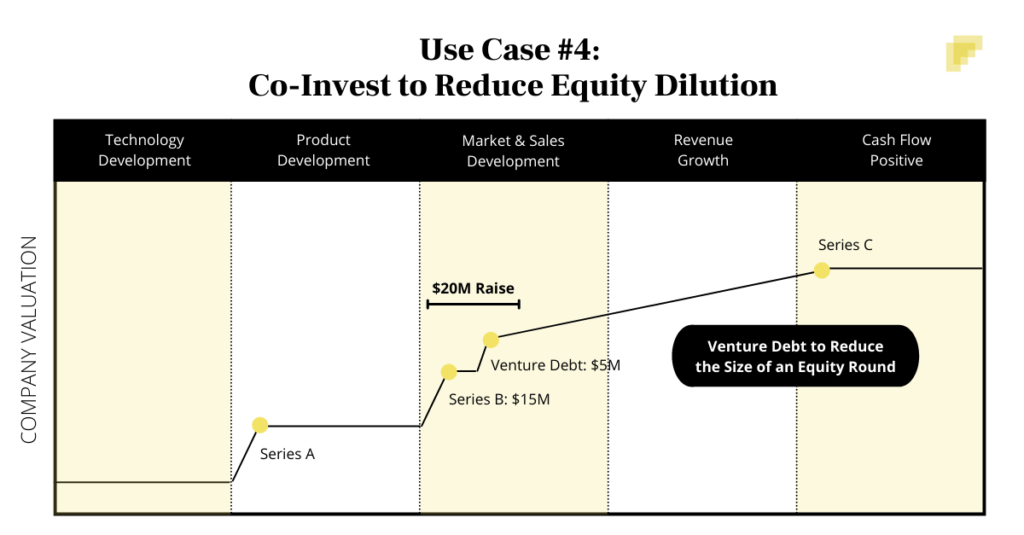
3. Preserving equity: By using venture debt instead of equity financing, companies can preserve their ownership stake and maintain control of their company.
4. Mitigating risk: Venture debt can be structured in a way that provides downside protection to lenders, which can make it a less risky form of financing for startups and early-stage companies.
Overall, the strategic use of venture debt can provide significant benefits to startups and early-stage companies, but it’s important to carefully consider the potential impact on shareholder equity before pursuing this type of financing.
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
While venture debt can provide a number of benefits to startups and early-stage companies, it’s important to compare it to other financing options, such as equity financing.
Equity financing involves selling ownership shares in the company to investors in exchange for capital. This can dilute the ownership stake of existing shareholders, but it can also provide access to a larger pool of capital.
In contrast, venture debt allows companies to raise capital without diluting their ownership stake or giving up control of their company. However, it typically involves higher interest rates and may require the issuance of warrants or equity options, which can dilute shareholder equity.
Ultimately, the decision between venture debt and equity financing will depend on the specific needs and goals of the company.
Conclusion
Venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups and early-stage companies, but it’s important to understand the impact on shareholder equity. By carefully evaluating the terms of the financing agreement and considering the strategic uses of venture debt, companies can use this financing option to achieve important business goals. As with any financing decision, it’s important to carefully consider all of the options and consult with financial and legal professionals before making a final decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing provided to startups and growing businesses that have already raised equity capital. It is typically a short-term loan with a fixed interest rate and warrants or equity options. Venture debt is often used to bridge the gap between equity financings or to extend a company’s runway without diluting existing shareholders.
Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt lenders are comfortable taking on higher risks and typically have flexible repayment terms. Venture debt can be a valuable tool for startups looking to raise capital while minimizing dilution.
How does venture debt work?
Venture debt works by providing a loan to a startup or growing business that has already raised equity capital. The loan typically has a fixed interest rate and warrants or equity options that can be exercised by the lender in the event of a liquidity event.
Venture debt lenders are often willing to take on higher risks than traditional banks and offer flexible repayment terms. The loan can be used to bridge the gap between equity financings or to extend a company’s runway without diluting existing shareholders.
What is shareholder equity?
Shareholder equity represents the amount of a company’s assets that are owned by shareholders after all liabilities have been paid. It is calculated by subtracting a company’s total liabilities from its total assets.
Shareholder equity is an important measure of a company’s financial health and is often used by investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s performance.
How does venture debt affect shareholder equity?
Venture debt can affect shareholder equity in a few ways. First, the loan will increase a company’s total liabilities, which will reduce shareholder equity. Second, if the lender requires warrants or equity options as part of the loan agreement, it could dilute existing shareholders if those options are exercised.
However, venture debt can also be used to extend a company’s runway without diluting existing shareholders, which can ultimately increase shareholder value in the long term.
What are the benefits of venture debt?
Venture debt can offer several benefits to startups and growing businesses. First, it can provide a source of capital without diluting existing equity holders. Second, venture debt lenders are often willing to take on higher risks and offer flexible repayment terms. Third, venture debt can be used to bridge the gap between equity financings, allowing companies to extend their runway and reach key milestones.
Additionally, venture debt lenders often bring valuable industry experience and connections to the table, which can help startups grow and succeed.
GRC Chat #56 – Venture Debt Explained and De-Risked with Zack Ellison
In conclusion, venture debt has a significant impact on shareholder equity. While it can provide a valuable source of financing for startups, it also often comes with higher interest rates and more stringent repayment terms than traditional debt. This can result in a higher debt-to-equity ratio, which can negatively impact the value of shareholders’ equity.
However, venture debt can also be a useful tool for startups looking to preserve equity and maintain control over their company. By taking on debt instead of diluting their ownership through equity financing, startups can maintain a larger share of their company and potentially reap greater rewards in the long term.
Ultimately, the impact of venture debt on shareholder equity depends on a variety of factors, including the terms of the debt, the financial health of the company, and the overall market conditions. While venture debt can be a valuable financing option for startups, it’s important for shareholders to carefully consider the potential impact on their equity before making any decisions.
