Venture debt is a type of financing that is becoming increasingly popular among startups and businesses. It is often compared to other forms of financing, such as equity and traditional debt, but some argue that it is a form of leverage. But can venture debt really be considered a form of leverage?
In this article, we will explore the concept of venture debt and its relationship with leverage. We will examine the similarities and differences between the two, and determine whether venture debt truly fits the definition of leverage. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of venture debt and leverage!
Cannot Venture Debt be Considered a Form of Leverage?
Introduction: Understanding Venture Debt and Leverage
Venture debt is a type of financing that is offered to startups and early-stage companies. It is a debt instrument, which means that the borrower is required to repay the loan over time with interest. On the other hand, leverage refers to the use of borrowed funds to increase the potential return on investment. It is commonly used in the context of investments in real estate and stocks. The question is whether venture debt can be considered a form of leverage.
Defining Venture Debt
Venture debt is a type of financing that is offered to startups and early-stage companies. It is typically used to finance growth and expansion, and it is often structured as a loan with a fixed interest rate and a repayment period of two to four years. Venture debt is usually secured by the company’s assets, such as intellectual property, equipment, or inventory.
Understanding Leverage
Leverage, on the other hand, refers to the use of borrowed funds to increase the potential return on investment. It is commonly used in the context of investments in real estate and stocks. For example, if an investor buys a property with a mortgage, they are using leverage because they are using borrowed funds to finance the purchase. If the property increases in value, the investor will realize a higher return on their investment than if they had used only their own funds.
Can Venture Debt be Considered a Form of Leverage?
Arguments for Venture Debt as Leverage
There are arguments to be made that venture debt can be considered a form of leverage. For example, venture debt can be used to finance growth and expansion, just like leverage is used to increase returns on investment. In addition, venture debt is often secured by the company’s assets, just like leverage is often secured by the underlying asset being financed.
Arguments Against Venture Debt as Leverage
However, there are also arguments against considering venture debt as a form of leverage. One of the main differences between venture debt and leverage is that venture debt is typically used to finance specific projects or initiatives, while leverage is used to finance a broader range of investments. In addition, venture debt is often offered on more favorable terms than traditional debt, which may make it less risky for the borrower.
Benefits of Venture Debt
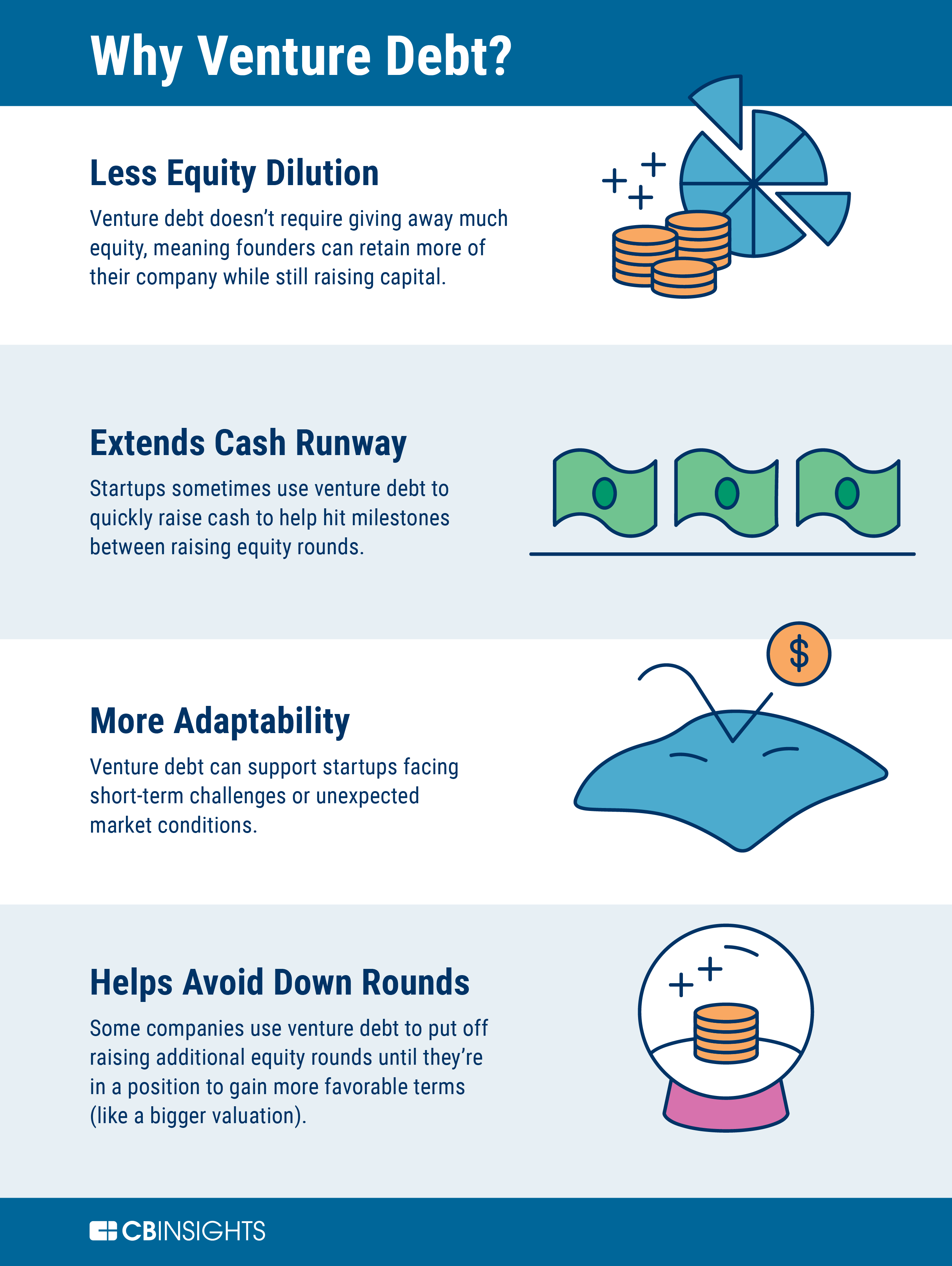
Lower Equity Dilution
One of the main benefits of venture debt is that it can help startups and early-stage companies avoid diluting their equity. When a company raises equity financing, they typically have to give up a portion of ownership in exchange for the funds. With venture debt, the company can raise funds without giving up equity, which can be especially valuable in the early stages of a company’s development.
Flexibility
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can provide greater flexibility than equity financing. Since venture debt is structured as a loan, the borrower has more control over how the funds are used and when they are repaid. In addition, venture debt can be used to finance specific projects or initiatives, which can be especially valuable for companies that are focused on developing new products or technology.
Lower Cost of Capital
Finally, venture debt can often be obtained at a lower cost of capital than equity financing. This is because venture debt is less risky for the lender than equity financing, which means that the lender can offer lower interest rates. In addition, venture debt is often structured with warrants or other equity kickers, which can provide additional value to the lender.
Venture Debt vs. Traditional Debt
Lower Interest Rates
One of the main differences between venture debt and traditional debt is the interest rates. Venture debt is often offered at lower interest rates than traditional debt, which can make it a more attractive option for startups and early-stage companies that are looking to minimize their financing costs.
Higher Risk
However, venture debt is also riskier than traditional debt. This is because venture debt is often offered to companies that are still in the early stages of development, which means that there is a higher risk of default. In addition, venture debt is often secured by the company’s assets, which means that the lender may have a higher priority in the event of a default.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there are arguments to be made for considering venture debt a form of leverage, there are also many differences between the two types of financing. Venture debt can offer many benefits to startups and early-stage companies, including lower equity dilution, greater flexibility, and a lower cost of capital. However, it is important to understand the risks associated with venture debt, including the higher risk of default and the potential for the lender to have a higher priority in the event of a default. Ultimately, whether venture debt is considered a form of leverage or not, it can be a valuable financing option for many companies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about venture debt and leverage.
What is the definition of leverage in finance?
In finance, leverage refers to using borrowed money to increase the potential return on an investment. This can be done by borrowing funds at a lower cost than the expected return on the investment, resulting in a higher return on equity. However, leverage also increases the risk of loss, as the borrowed funds must be repaid regardless of the success of the investment.
Venture debt, on the other hand, is a type of financing that allows startups to borrow money without diluting their ownership. While venture debt may involve some form of collateral or security, it is not typically considered a form of leverage in finance, as it does not involve the use of borrowed funds to amplify returns.
What are the advantages of venture debt?
Venture debt can be an attractive financing option for startups, as it offers several advantages over other types of funding. First, venture debt allows startups to access capital without diluting their ownership, which is especially important for early-stage companies. Additionally, venture debt can provide a lower cost of capital than equity financing, as lenders typically charge lower interest rates than equity investors demand in return for their investment.
Finally, venture debt can be structured in a way that aligns with the specific needs and growth plans of a startup. For example, venture debt can be used to finance specific projects or acquisitions, allowing startups to pursue growth opportunities without sacrificing equity ownership.
Can venture debt be used as a form of leverage?
While venture debt may involve the use of borrowed funds, it is not typically considered a form of leverage in finance. This is because venture debt does not involve using borrowed funds to amplify the potential return on an investment. Instead, venture debt is a type of financing that allows startups to access capital without diluting their ownership.
However, there are some situations in which venture debt may be used in conjunction with other forms of financing to create a leveraged investment. For example, a startup may use venture debt to finance a portion of a larger acquisition, while also using equity financing to fund the remainder of the purchase price.
What are the risks of venture debt?
While venture debt can be an attractive financing option for startups, it is not without risks. One of the primary risks of venture debt is that it must be repaid regardless of the success of the investment. This means that if a startup is unable to generate sufficient cash flow to make its debt payments, it may be forced to default on its debt obligations, which can have serious consequences for the company’s financial health.
Additionally, venture debt can be more expensive than other forms of financing in certain circumstances. For example, if a startup’s cash flow projections are overly optimistic, it may have to pay higher interest rates to compensate lenders for the increased risk of default.
How does venture debt differ from traditional bank loans?
Venture debt differs from traditional bank loans in several key ways. First, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders who have experience working with startups and understand the unique risks and opportunities associated with investing in early-stage companies. Additionally, venture debt is often structured in a way that aligns with the growth plans and cash flow needs of startups, whereas traditional bank loans may have more rigid repayment terms and collateral requirements.
Finally, venture debt is often considered a more flexible and patient form of financing than traditional bank loans, as lenders are typically more focused on the long-term success of the startup than on short-term returns. This can be especially important for startups that are still in the early stages of their growth and may not have a clear path to profitability.
What to do if you can’t raise Venture Debt?
In conclusion, while venture debt may seem similar to traditional forms of leverage, it is important to recognize the differences between the two. Venture debt offers unique benefits such as flexibility in repayment terms and the ability to raise additional capital without diluting equity. Additionally, venture debt can be a strategic tool for startups looking to extend their runway and reach key milestones. However, it is also important to consider the potential risks and costs associated with venture debt, such as higher interest rates and the potential for default.
Overall, whether or not venture debt should be considered a form of leverage ultimately depends on one’s perspective and definition of leverage. While it does involve taking on debt to finance growth, its specific features and benefits set it apart from traditional forms of leverage. Ultimately, startups should carefully weigh the pros and cons of venture debt before deciding whether or not it is the right financing option for their business.
