Venture debt is a popular financing option for startups that have a promising growth trajectory. However, as the company grows, the debt may become a burden. To alleviate the pressure, some startups may consider converting their venture debt to equity. But is it possible? Let’s dive into this topic to find out.
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of venture debt and equity and the pros and cons of converting one to the other. We’ll also look at the circumstances under which a company may choose to convert its venture debt to equity and the process involved in doing so.
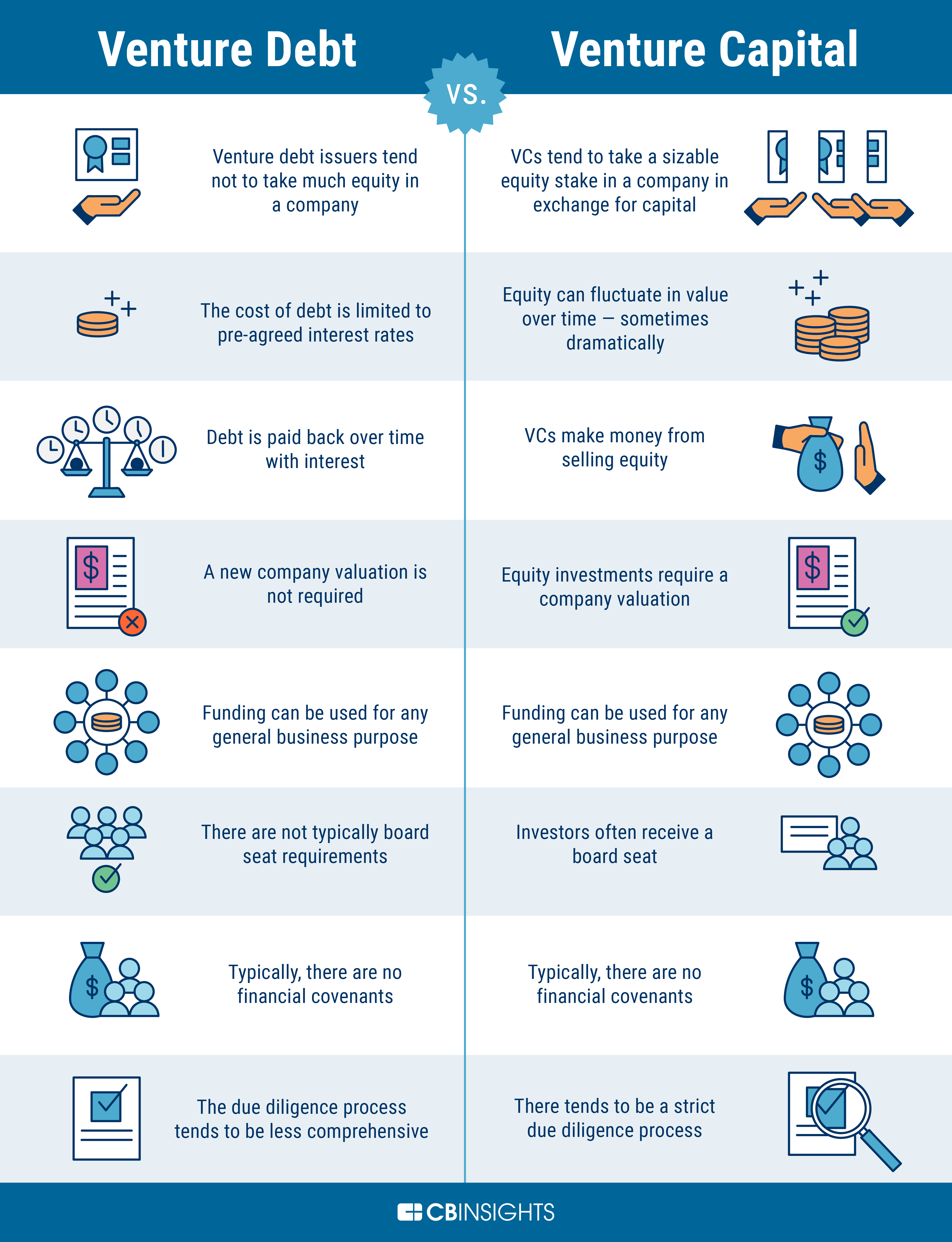
Can Venture Debt be Converted to Equity?
Venture debt is a type of financing that is often used by startups and other companies that are looking for additional capital to fund their growth. This type of financing is typically structured as a loan, but it also has some characteristics of equity financing. One question that often comes up when discussing venture debt is whether it can be converted to equity. In this article, we’ll explore this topic in detail and provide you with all the information you need to know about venture debt conversion.
What is Venture Debt?
Venture debt is a form of debt financing that is specifically designed to meet the needs of startups and other fast-growing companies. This type of financing is typically provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs and risks associated with startup investing.
Unlike traditional debt financing, venture debt often includes some equity-like features, such as warrants or conversion rights. These features provide the lender with the opportunity to participate in the potential upside of the company’s growth, while still receiving a fixed rate of interest on their investment.
Benefits of Venture Debt
There are several benefits associated with venture debt, including:
- Access to additional capital without diluting equity
- Flexible repayment terms
- Potential for equity-like returns through warrants or conversion rights
- Ability to leverage existing equity financing
Venture Debt vs. Traditional Debt
While venture debt shares some characteristics with traditional debt financing, there are also some key differences. One of the main differences is the increased risk associated with startup investing. Because startups are often in the early stages of development and have yet to establish a track record of success, lenders may require more collateral or charge higher interest rates to compensate for this risk.
Another key difference is the potential for equity-like returns through warrants or conversion rights. While traditional debt financing provides lenders with a fixed rate of interest, venture debt lenders have the opportunity to participate in the upside potential of the company’s growth.
What is Venture Debt Conversion?
Venture debt conversion is the process by which a venture debt loan is converted into equity. This can occur through a variety of mechanisms, such as the exercise of warrants or the conversion of the loan into preferred stock.
The conversion of venture debt into equity can be beneficial for both the lender and the borrower. For the lender, it provides an opportunity to participate in the upside potential of the company’s growth, while also reducing their overall risk exposure. For the borrower, it can provide access to additional equity financing without diluting the ownership stake of existing shareholders.
Types of Venture Debt Conversion
There are two main types of venture debt conversion:
- Warrant Conversion: This type of conversion occurs when the lender exercises warrants that were issued as part of the original loan agreement. The lender pays the exercise price for the warrants, which is typically set at a discount to the company’s current valuation, and receives shares of the company’s common stock in exchange.
- Loan Conversion: This type of conversion occurs when the venture debt loan is converted into preferred stock. The conversion rate is typically based on the company’s current valuation, and the lender receives shares of the company’s preferred stock in exchange for their loan.
Benefits of Venture Debt Conversion
There are several benefits associated with venture debt conversion, including:
- Access to additional equity financing without diluting existing shareholders
- Opportunity for lenders to participate in the upside potential of the company’s growth
- Reduced overall risk exposure for lenders
- Ability to provide additional capital to support growth initiatives
Venture Debt Conversion vs. Equity Financing
While both venture debt conversion and equity financing provide access to additional capital, there are some key differences. With equity financing, the company issues new shares of stock to investors in exchange for their capital. This dilutes the ownership stake of existing shareholders and can result in a loss of control over the company’s decision-making process.
With venture debt conversion, the loan is converted into equity, but the ownership stake of existing shareholders is not diluted. This allows the company to access additional capital without giving up control over the decision-making process.
Conclusion
Venture debt is a valuable form of financing for startups and other fast-growing companies. With its equity-like features and flexible repayment terms, it provides a unique opportunity for lenders and borrowers alike. Venture debt conversion is also an important consideration, as it provides access to additional equity financing without diluting existing shareholders. By understanding the benefits and risks associated with venture debt and conversion, companies can make informed decisions about their financing needs and growth strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is typically provided to startups and other high-growth companies that have already raised equity financing. Unlike traditional debt financing, venture debt usually comes with warrants or other equity-related options that give the lender the right to purchase equity in the company at a later date.
Venture debt is often used to extend the runway of a startup or to finance specific growth initiatives, such as product development or expansion into new markets.
What is equity financing?
Equity financing is a way for companies to raise capital by selling ownership in the company in exchange for cash. This can be done through private placements, initial public offerings (IPOs), or other means. Equity financing can be more expensive than debt financing, but it does not require the borrower to make regular interest payments and can provide a longer-term source of capital.
Equity financing can also bring in strategic investors who can provide expertise, connections, and other resources that can help the company grow and succeed.
What is debt-to-equity conversion?
Debt-to-equity conversion is the process of converting debt into equity. In the context of venture debt, this can happen when the lender exercises warrants or other equity-related options that were included as part of the debt financing. When this happens, the lender becomes a shareholder in the company instead of a creditor.
Debt-to-equity conversion can be a good option for startups that are struggling to make regular interest payments on their debt or that are looking for a longer-term source of capital.
Can venture debt be converted to equity automatically?
In some cases, venture debt may come with warrants or other equity-related options that can be automatically exercised if certain conditions are met, such as the company reaching a certain valuation or achieving certain milestones. In other cases, the conversion may need to be negotiated between the lender and the borrower.
The terms of the debt financing agreement will typically dictate how and when debt can be converted to equity.
What are the risks of debt-to-equity conversion?
One risk of debt-to-equity conversion is that the lender may become a significant shareholder in the company, which can dilute the ownership of existing shareholders. Additionally, if the company is not successful, the lender may not be able to recoup their investment if the company goes bankrupt or is sold for less than the amount of the outstanding debt.
It is important for both the lender and the borrower to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of debt-to-equity conversion before proceeding with the transaction.
Venture Debt & Other Alternatives to Equity in 2020+ w/ Founderpath Founder Nathan Latka
In conclusion, venture debt can indeed be converted to equity, which can be a great option for startups and other companies that need to raise funds. This method allows companies to secure financing without giving up control or ownership of their business, and it can also help them attract investors who are interested in the potential for future growth.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that converting debt to equity is not always the best choice for every company. There are risks and potential downsides to this strategy, such as dilution of ownership and the potential for conflicts with existing shareholders. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider all of the factors involved before making a decision.
Ultimately, the decision to convert venture debt to equity depends on a variety of factors, including the company’s financial situation, its growth potential, and its long-term goals. By understanding the pros and cons of this strategy, companies can make informed decisions about their financing options and position themselves for success in the future.
