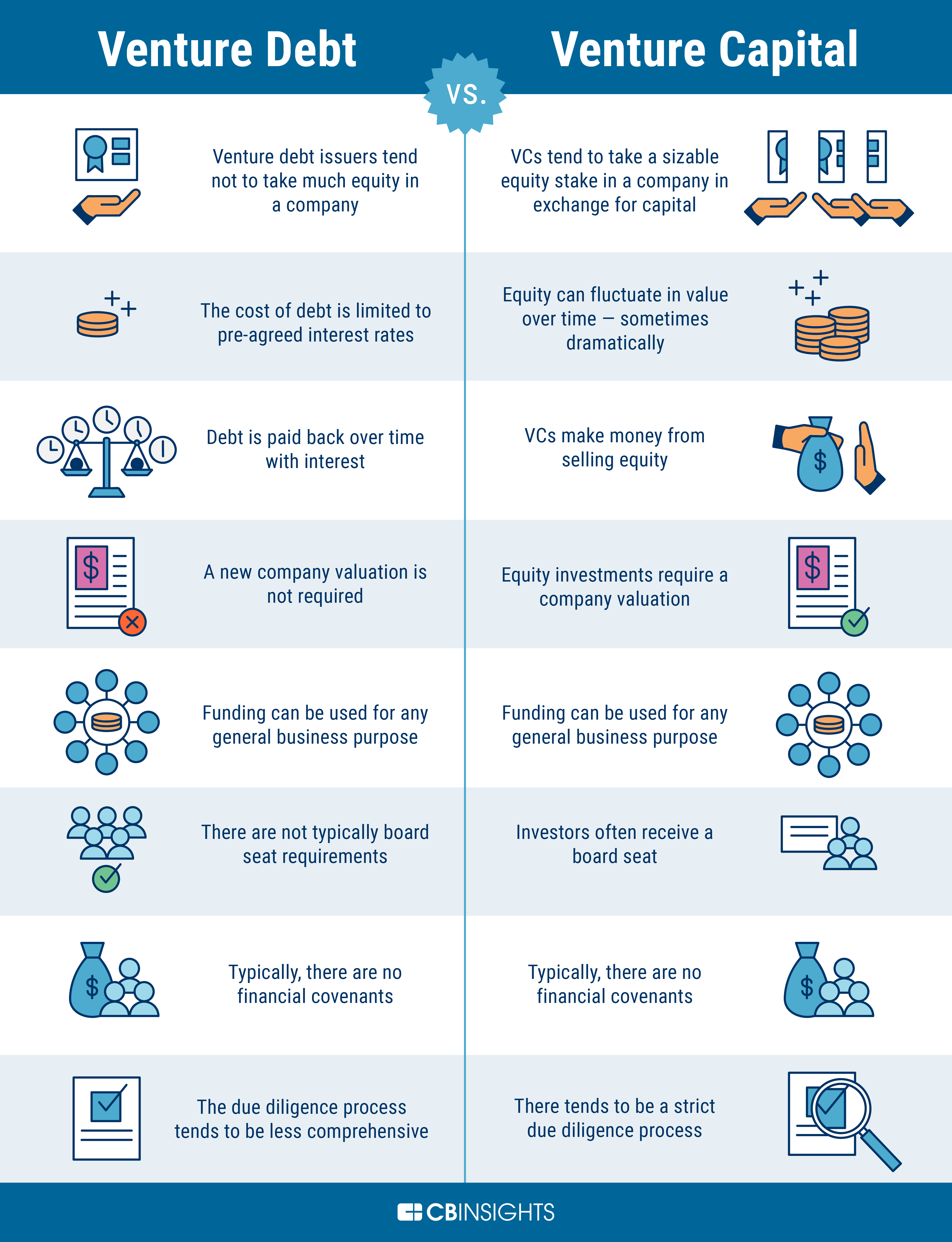
Venture debt and equity financing are two common ways for startups to raise capital. However, each financing option has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. While equity financing involves giving up a portion of ownership in the company, venture debt allows startups to borrow money without diluting their ownership stake.
So, when should startups consider using venture debt instead of equity? In this article, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of venture debt financing and discuss the scenarios where it might be the better option for startups looking to raise capital.
When to use Venture Debt instead of Equity?
Venture capital is often seen as the go-to source of funding for startups and growing businesses. However, equity financing may not always be the best option. Venture debt is an alternative form of financing that can provide startups and growing businesses with the capital they need to grow without diluting their ownership stake. In this article, we will discuss when it makes sense to use venture debt instead of equity.
1. Cash runway
One of the key benefits of venture debt is that it can extend a company’s cash runway. Cash runway refers to the amount of time a company can operate with its existing cash reserves before running out of money. In some cases, a company may not need to raise additional equity capital but simply needs more cash to extend its runway. In such cases, venture debt can be a great option.
Venture debt can help a company extend its runway by providing additional capital that can be used to fund operations, product development, and marketing initiatives. This can give the company more time to reach key milestones and increase its valuation, making it more attractive to equity investors down the line.
2. Lower dilution
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can help reduce dilution. Dilution refers to the reduction in ownership percentage that occurs when a company issues new equity shares. When a company raises equity capital, it typically issues new shares of stock to investors in exchange for cash. This results in a reduction in the ownership percentage of existing shareholders.
Venture debt, on the other hand, does not result in dilution. When a company raises venture debt, it does not issue new shares of stock. Instead, it borrows money from a lender and agrees to pay it back with interest. This means that existing shareholders can retain their ownership percentage while still accessing the capital they need to grow.
3. Non-dilutive funding
Venture debt is considered a form of non-dilutive funding. Non-dilutive funding refers to any form of financing that does not result in the issuance of new equity shares. Examples of non-dilutive funding include grants, loans, and revenue-based financing.
Non-dilutive funding can be attractive to companies that want to retain ownership and control over their business. By raising non-dilutive capital, a company can access the funds it needs to grow without giving up equity or control.
4. Faster funding
Venture debt can be faster to obtain than equity financing. Equity financing typically involves a lengthy due diligence process, which can take several months to complete. During this time, the company may be unable to access the capital it needs to grow.
Venture debt, on the other hand, can be obtained more quickly. The due diligence process is typically shorter, and the funds can be disbursed more quickly than with equity financing. This can be especially important for companies that need to move quickly to take advantage of market opportunities.
5. Lower cost of capital
Another benefit of venture debt is that it can be less expensive than equity financing. Equity financing typically involves a higher cost of capital because investors expect a higher return on their investment. This can result in a higher cost of capital for the company.
Venture debt, on the other hand, typically has a lower cost of capital because it is considered less risky than equity financing. This can make it a more attractive option for companies that want to access capital at a lower cost.
6. Flexibility
Venture debt can be more flexible than equity financing. Equity financing typically involves giving up a percentage of ownership in exchange for capital. This can result in a loss of control and decision-making power for the company.
Venture debt, on the other hand, does not involve the issuance of new equity shares. This means that the company can retain control and decision-making power while still accessing the capital it needs to grow. Additionally, venture debt can be structured in a variety of ways, giving companies more flexibility in how they use the capital.
7. Suitable for specific needs
Venture debt can be suitable for specific types of financing needs. For example, venture debt can be a good option for companies that need capital to fund a specific project, such as a product launch or marketing campaign. It can also be a good option for companies that have a predictable revenue stream and can use that revenue to pay back the debt.
8. Not suitable for all businesses
While venture debt can be a great option for some businesses, it is not suitable for all businesses. Venture debt is typically only available to companies that have a proven track record of revenue growth and profitability. Additionally, venture debt can be more expensive than traditional bank loans, making it a less attractive option for businesses with limited cash flow.
9. Vs Equity financing
When deciding between venture debt and equity financing, it is important to consider the pros and cons of each option. Equity financing can provide a company with a larger amount of capital, but it can also result in dilution and loss of control. Venture debt, on the other hand, can provide a company with non-dilutive financing and greater flexibility, but it may not provide as much capital as equity financing.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, venture debt can be a great alternative to equity financing for startups and growing businesses. It can provide companies with the capital they need to grow without diluting ownership or control. Additionally, venture debt can be faster and less expensive than equity financing, making it an attractive option for companies that need to move quickly to take advantage of market opportunities. However, venture debt is not suitable for all businesses and should be carefully considered before making a decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of financing that involves borrowing money from a specialized lender to help grow a business. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically used by startups and other high-growth companies, and is often structured as a complement to equity financing.
While venture debt can be more expensive than traditional bank loans, it can also provide companies with additional capital to fund growth initiatives without diluting the ownership stake of existing shareholders.
When is venture debt a good choice?
Venture debt can be a good choice for companies that have already raised equity financing and are looking for additional capital to invest in growth initiatives. Because venture debt typically has a lower cost of capital than equity financing, it can be a more affordable option for companies that are looking to expand their operations without diluting their ownership stake.
Additionally, venture debt can be a good choice for companies that have a clear path to profitability and are looking for a short-term financing option to help bridge the gap until they become cash flow positive.
When should I use equity financing instead of venture debt?
Equity financing is typically a better option than venture debt for companies that are just starting out and have not yet raised any outside capital. Because equity financing does not require repayment, it can be a good way for companies to get the capital they need to get off the ground without taking on debt.
Additionally, equity financing can be a good choice for companies that are highly speculative and do not have a clear path to profitability. In these cases, investors are willing to take on the risk of investing in the company in exchange for the potential of a high return on their investment.
What are the benefits of using venture debt?
One of the main benefits of using venture debt is that it can provide companies with additional capital to fund growth initiatives without diluting the ownership stake of existing shareholders. Additionally, venture debt can be a more affordable option than equity financing, as it typically has a lower cost of capital.
Another benefit of using venture debt is that it can help companies extend their runway until they become cash flow positive. This can be especially useful for companies that are operating in industries with long sales cycles or that require significant upfront investment.
What are the risks of using venture debt?
One of the main risks of using venture debt is that it can be more expensive than traditional bank loans, as lenders typically charge higher interest rates and fees to compensate for the higher risk of lending to startups and other high-growth companies.
Additionally, venture debt can be risky for companies that are not yet profitable or do not have a clear path to profitability. Because venture debt requires repayment, companies that are unable to generate sufficient cash flow to service their debt may be at risk of default.
Venture Debt VS Equity Financing for a high-growth startup?
In conclusion, deciding between venture debt and equity financing is a critical decision for entrepreneurs seeking to raise capital. Venture debt is an excellent option for businesses that have a clear plan for generating revenue and are looking to expand their operations without diluting ownership. On the other hand, equity financing is suitable for startups that need substantial capital to kick-start their business and are willing to share ownership of their company.
While venture debt can be a risky option, it can also provide businesses with the necessary capital to take advantage of growth opportunities. It allows entrepreneurs to retain control of their company while also limiting the amount of equity they sell. Additionally, venture debt typically has lower interest rates than traditional loans, making it a more affordable option for small businesses.
Ultimately, the decision to use venture debt or equity financing depends on the specific needs of each startup. It’s essential to carefully evaluate the pros and cons of each option and consult with financial experts to determine the best financing strategy for your business. By doing so, you can ensure that you’re making the right decision for your company and positioning it for long-term success.
