As an entrepreneur, you may have come across terms like venture debt and equity. While both of these funding options can help you raise capital for your business, they are not the same. In fact, many people mistakenly think that these two options are similar, but in reality, they have some significant differences that you should be aware of.
Venture debt and equity both involve taking on capital from investors, but the way they work and the terms involved are quite different. In this article, we will explore the similarities and differences between these two funding options, so you can make an informed decision about which one is right for your business.
Aren’t Venture Debt and Equity Similar?
Venture debt and equity are two common ways businesses raise capital. While they share some similarities, they have distinct differences that make each financing option unique. In this article, we’ll explore the differences and similarities between venture debt and equity.
What is Venture Debt?
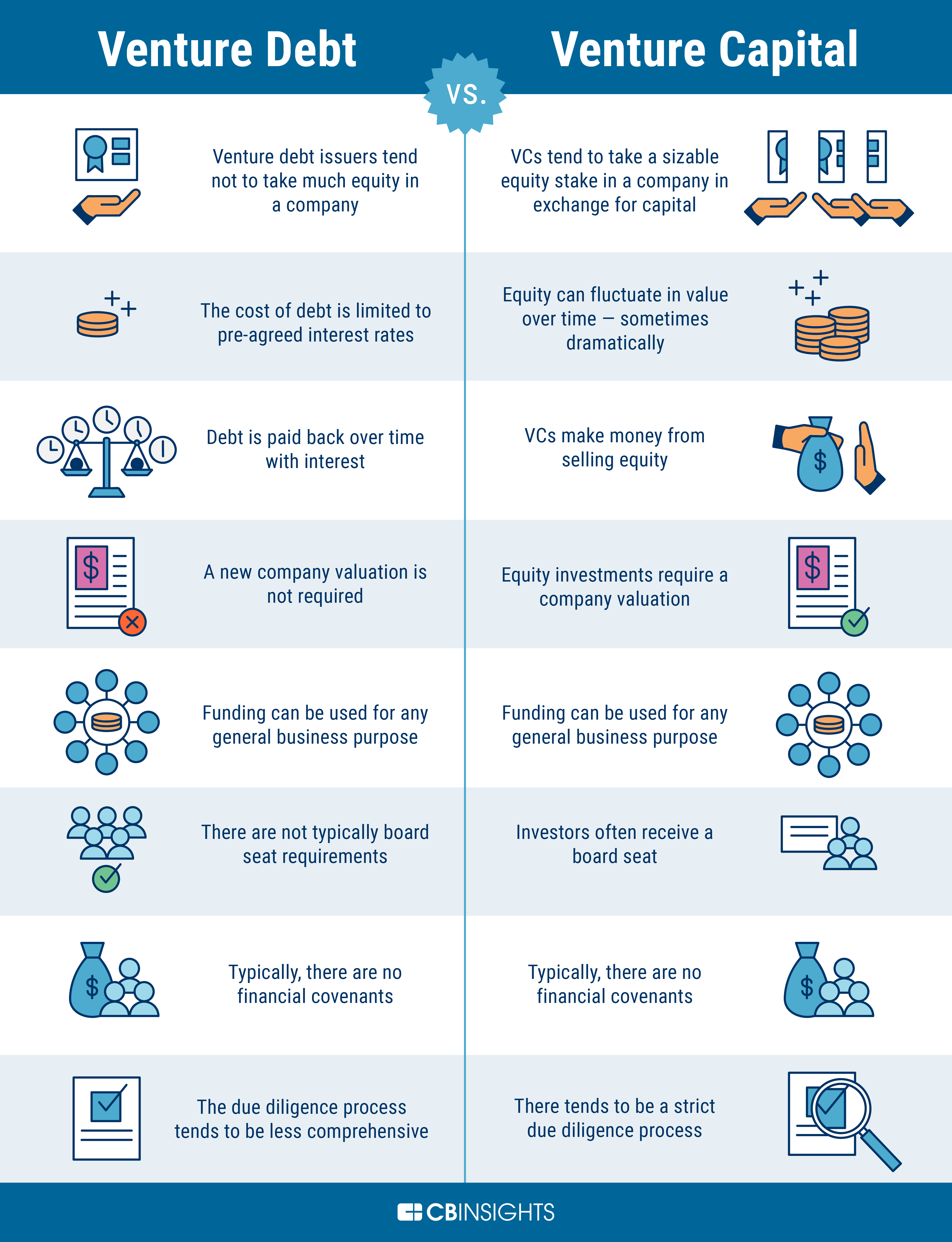
Venture debt is a type of financing that allows businesses to borrow money from lenders. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically used by startups and growing companies that are not yet profitable. Venture debt is often used to supplement equity financing, providing businesses with the additional capital they need to grow.
Venture debt is typically structured as a loan with interest and principal payments. The loan may also include warrants, which give the lender the option to purchase equity in the company at a later date. Venture debt can be a useful financing option for businesses that have a solid revenue base and are looking to grow their operations.
Some benefits of venture debt include:
- Lower cost of capital compared to equity financing
- Non-dilutive, meaning that business owners maintain control and ownership of their company
- Flexible repayment terms
What is Equity Financing?
Equity financing is a type of financing that allows businesses to raise capital by selling shares of ownership in the company. This can include common stock, preferred stock, and other securities. Equity financing is typically used by startups and growing companies that are not yet profitable.
Equity financing provides businesses with the capital they need to grow without incurring debt. However, it also means that business owners will be diluting their ownership in the company. This means that they will have to share control of the business with other shareholders.
Some benefits of equity financing include:
- No debt to repay
- Access to larger amounts of capital
- Investors can provide valuable expertise and connections
Venture Debt vs. Equity Financing
While venture debt and equity financing share some similarities, there are also some significant differences between the two financing options. Here are some of the key differences:
Cost of Capital
Venture debt typically has a lower cost of capital than equity financing. This is because venture debt is considered less risky than equity financing. Lenders are willing to provide venture debt at a lower cost because they have collateral in the form of the company’s assets.
Ownership
In equity financing, investors receive ownership in the company in exchange for their investment. This means that business owners are diluting their ownership in the company. With venture debt, business owners maintain control and ownership of the company.
Repayment
Venture debt is structured as a loan with interest and principal payments. This means that businesses have to repay the loan over time. With equity financing, there is no debt to repay. Investors receive a return on their investment through dividends or by selling their shares at a later date.
Covenants
Venture debt often comes with covenants that require businesses to maintain certain financial ratios or meet other performance metrics. This ensures that the business is on track to repay the loan. Equity financing does not typically have covenants.
Risk
Equity financing is considered riskier than venture debt because investors are taking on more risk. If the company fails, investors may lose their entire investment. With venture debt, lenders have collateral in the form of the company’s assets, which reduces their risk.
Amount of Capital
Equity financing allows businesses to raise larger amounts of capital than venture debt. This is because there is no limit to the number of shares that can be sold. With venture debt, there is a limit to the amount of debt that a business can take on.
The Bottom Line
Both venture debt and equity financing are viable options for businesses looking to raise capital. The choice between the two financing options depends on the specific needs of the business. Venture debt is a good option for businesses that are looking to supplement their equity financing and have a solid revenue base. Equity financing is a good option for businesses that are looking to raise larger amounts of capital without incurring debt.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people ask about venture debt and equity.
What is Venture Debt?
Venture debt is a type of debt financing that is provided to early-stage and high-growth companies. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders who understand the unique needs of startups. Venture debt can be a useful tool for companies that are looking to grow quickly without diluting their equity.
Venture debt is similar to traditional debt in that it requires regular interest payments and has a set maturity date. However, venture debt is often structured with warrants or equity kicker options, which give the lender the right to purchase equity in the borrower at a later date. This allows the lender to participate in the upside potential of the borrower’s success.
What is Equity Financing?
Equity financing is a method of raising capital for a company by selling shares of ownership. This is typically done through a private placement or an initial public offering (IPO). Equity investors provide funding in exchange for a share of ownership in the company and a portion of any future profits.
Equity financing is different from debt financing in that there is no set maturity date or interest payments. Instead, investors are taking on the risk of the company’s success or failure. If the company does well, investors can make a significant return on their investment. However, if the company fails, investors may lose their entire investment.
What are the similarities between Venture Debt and Equity?
While venture debt and equity are different types of financing, there are some similarities between the two. Both are typically used by early-stage and high-growth companies that are looking to raise capital to fund their growth. Additionally, both types of financing involve taking on some level of risk in exchange for potential rewards.
However, there are also some key differences between the two. Venture debt is a form of debt financing, while equity financing involves selling ownership in the company. Venture debt typically has a set maturity date and requires regular interest payments, while equity financing does not have a set maturity date or require interest payments.
What are the differences between Venture Debt and Equity?
One of the main differences between venture debt and equity is the level of ownership and control that the borrower retains. With venture debt, the borrower retains full ownership and control of the company, but is required to make regular interest payments and may be subject to covenants or other restrictions.
With equity financing, the borrower is selling ownership in the company and giving up some control. However, equity investors are typically more patient and are willing to wait longer for a return on their investment. Additionally, equity financing does not require regular interest payments and may not have a set maturity date.
Which is better, Venture Debt or Equity?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best type of financing will depend on the specific needs and goals of the company. Venture debt may be a good option for companies that are looking to raise capital without diluting their equity, while equity financing may be a better option for companies that are looking for a long-term partner who is willing to take on more risk.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to pursue venture debt or equity financing will depend on the company’s unique situation and goals. It is important to carefully consider the pros and cons of each type of financing and to work with a trusted advisor to make the best decision for the company.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, while venture debt and equity share some similarities, they are ultimately different financial instruments with unique characteristics. Venture debt allows startups to access capital without sacrificing equity, but it comes with stricter terms and higher interest rates. Equity, on the other hand, allows investors to share in the potential upside of a company, but dilutes the ownership of the founding team.
It’s important for startups to carefully consider their options when deciding between venture debt and equity. Factors such as growth stage, funding needs, and future goals should all be taken into account. Ultimately, the decision will depend on the individual circumstances of each company.
Overall, both venture debt and equity have their own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can help startups make informed decisions about their financing options and set them on the path to long-term success.
