Venture debt is a popular financing option for many startups looking to grow their business without giving up equity. However, like any financial instrument, it has its downsides. In this article, we’ll explore the cons of venture debt and help you decide if it’s the right choice for your business.
From higher interest rates to limited flexibility, venture debt has several disadvantages that can impact your company’s financial health. We’ll break down these cons in detail and offer some alternative financing options that might be a better fit for your business. So, let’s dive in and explore the negative aspects of venture debt.
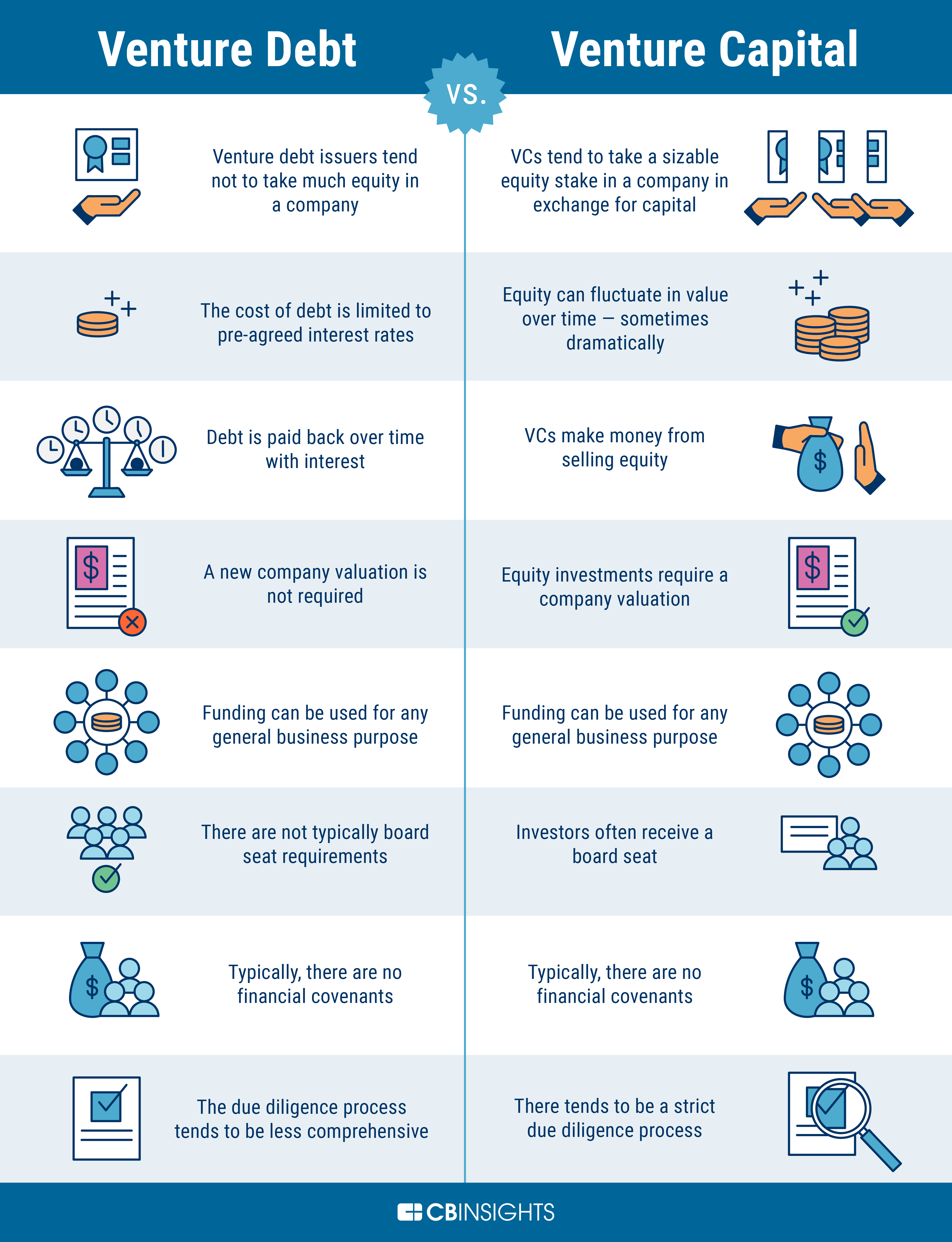
What are the cons of venture debt?
Venture debt is a type of financing that provides startups with a loan that is secured by their assets. While this type of financing can be attractive to many startups, it is not without its cons. Here are some of the main disadvantages of venture debt.
1. Higher interest rates
Venture debt typically comes with higher interest rates than traditional bank loans. This is because venture debt lenders are taking on more risk by lending to startups that may not yet have a proven track record of success. Higher interest rates can make it more difficult for startups to make their loan payments and can eat into their profits.
Some venture debt lenders also charge additional fees, such as origination fees or prepayment penalties, which can further increase the cost of borrowing.
2. Limited flexibility
Venture debt lenders often require collateral to secure the loan, such as a portion of the startup’s equity or intellectual property. This can limit the flexibility of the startup’s capital structure and may make it more difficult to raise future funding rounds.
In addition, venture debt lenders may impose covenants on the startup that restrict its ability to take on additional debt or make certain business decisions. This can limit the startup’s flexibility and may make it more difficult to pursue growth opportunities.
3. Risk of default
Because venture debt lenders are taking on more risk, startups that take on venture debt are at a higher risk of defaulting on their loans. If a startup is unable to make its loan payments, the lender may have the right to seize the startup’s collateral or take other legal action.
This can be particularly concerning for startups that are still in the early stages of development and may not have a steady stream of revenue to rely on.
4. Pressure to perform
Taking on venture debt can put pressure on startups to perform and generate revenue quickly. This pressure can be particularly acute if the startup is using the debt to fund a specific project or product launch.
If the startup is unable to generate revenue quickly enough to make its loan payments, it may be forced to take on additional debt or seek out other sources of funding.
5. Limited investor participation
Venture debt lenders typically do not provide startups with the same level of investor participation as traditional venture capitalists. This means that startups may miss out on valuable advice, mentorship, and networking opportunities that can help them grow and succeed.
In addition, venture debt lenders may not be as invested in the startup’s success as traditional venture capitalists, which can lead to a misalignment of incentives.
6. Limited upside potential
Unlike traditional venture capital financing, venture debt does not provide startups with the same potential for significant returns. This is because the lender is typically only entitled to a fixed interest rate or a portion of the startup’s equity.
This can limit the upside potential for startups that are looking to scale quickly and generate significant returns for their investors.
7. Short-term focus
Venture debt lenders typically require startups to repay their loans within a relatively short timeframe, often within two to three years. This short-term focus can make it difficult for startups to pursue longer-term growth opportunities that may require more time and investment.
In addition, the pressure to repay the loan quickly can lead startups to make short-term decisions that may not be in their best interests in the long run.
8. Limited availability
Venture debt financing is not as widely available as traditional bank loans or equity financing. This is because venture debt lenders are often looking for startups with a proven track record of success and a strong revenue stream.
This can make it difficult for startups that are still in the early stages of development or that are pursuing more innovative or risky business models to secure venture debt financing.
9. Limited use of funds
Venture debt lenders typically have specific restrictions on how the funds can be used. For example, the lender may require the funds to be used for a specific project or product launch.
This can limit the startup’s ability to use the funds as needed to pursue growth opportunities or respond to changes in the market.
10. Potential for dilution
If the startup is required to issue equity to the venture debt lender as collateral, this can lead to dilution of the founders’ ownership stake. This can be particularly concerning for startups that are still in the early stages of development and may not have a significant amount of equity to begin with.
In addition, if the startup is unable to repay the loan and the lender takes ownership of the equity, this can further dilute the founders’ ownership stake and limit their control over the company.
Overall, while venture debt can be an attractive financing option for startups, it is not without its risks and drawbacks. Startups that are considering venture debt financing should carefully weigh the pros and cons and consider all of their financing options before making a decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions regarding the cons of venture debt:
What are the potential downsides of venture debt?
Venture debt can be a risky form of financing, as it often requires a higher interest rate and collateral than traditional loans. This means that if the company does not perform as expected, it may struggle to meet its debt obligations and risk defaulting on the loan.
Additionally, venture debt may limit a company’s flexibility and future financing options. As debt is a fixed obligation, it can make it more difficult for a company to raise additional equity financing or negotiate favorable terms with investors.
How does venture debt compare to equity financing?
While equity financing allows companies to raise capital without taking on debt, it typically requires giving up a portion of ownership and control to investors. In contrast, venture debt allows companies to retain ownership and control, but comes with more financial risk and less flexibility.
Overall, the choice between equity and debt financing depends on the specific needs and goals of the company, as well as its risk tolerance and financial situation.
What are some alternative forms of financing to consider?
There are several alternatives to venture debt that companies can pursue, including traditional bank loans, crowdfunding, and revenue-based financing. Each of these options has its own pros and cons, depending on the company’s stage of growth, financial needs, and risk profile.
Ultimately, it’s important for companies to explore all available financing options and choose the one that best aligns with their goals and objectives.
What are the risks of taking on too much debt?
One of the biggest risks of taking on too much debt is the potential for default, which can lead to bankruptcy and other financial difficulties. Additionally, high levels of debt can limit a company’s ability to invest in growth and innovation, as well as reduce its creditworthiness and ability to secure future financing.
Therefore, it’s important for companies to carefully consider their debt obligations and ensure that they have a sustainable plan for repayment and continued growth.
How can companies mitigate the risks of venture debt?
One way for companies to mitigate the risks of venture debt is to carefully assess their financial situation and ability to meet debt obligations. This includes developing a clear plan for repayment and ensuring that the terms of the loan are favorable and aligned with the company’s goals.
Additionally, companies can work with experienced advisors and investors who can provide guidance and support throughout the financing process, as well as help identify and mitigate potential risks and pitfalls.
How to think about venture debt
In conclusion, it is important to weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether venture debt is the right financing option for your business. While venture debt can provide access to capital without diluting ownership, there are also some significant drawbacks to consider.
Firstly, venture debt can be expensive due to higher interest rates and fees. This can put a strain on your cash flow and make it challenging to meet your repayment obligations. Additionally, venture debt often comes with covenants that restrict your ability to make strategic business decisions.
Secondly, if your business hits a rough patch, venture debt can quickly become a burden. Unlike equity financing, you still have to make payments on your debt, even if your business is struggling. This can lead to a vicious cycle where you are forced to take on more debt to cover your existing obligations.
Lastly, venture debt can limit your ability to attract future investors. Potential investors may be hesitant to invest in a company with a lot of debt on its balance sheet, especially if they are concerned about your ability to make timely payments.
In summary, venture debt can be a useful financing tool for some businesses, but it’s important to carefully consider the potential downsides before making a decision. It’s always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor or business expert to help you determine whether venture debt is the right option for your specific needs.
